Home > Press > Researchers uncover secret of nanomaterial that makes harvesting sunlight easier
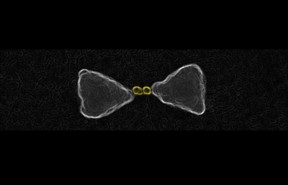 |
| These are gold nanoparticles chemically guided inside the hot-spot of a larger gold bow-tie nanoantenna. CREDIT E Cortes et al, 2017 |
Abstract:
Using sunlight to drive chemical reactions, such as artificial photosynthesis, could soon become much more efficient thanks to nanomaterials.
Researchers uncover secret of nanomaterial that makes harvesting sunlight easier
London, UK | Posted on March 29th, 2017This is the conclusion of a study published today led by researchers in the Department of Physics at Imperial College London, which could ultimately help improve solar energy technologies and be used for new applications, such as using sunlight to break down harmful chemicals.
Sunlight is used to drive many chemical processes that would not otherwise occur. For example, carbon dioxide and water do not ordinarily react, but in the process of photosynthesis, plants take these two chemicals and, using sunlight, produce oxygen and sugar.
The efficiency of this reaction is very high, meaning much of the energy from sunlight is transferred to the chemical reaction, but so far scientists have been unable to mimic this process in manmade artificial devices.
One reason is that many molecules that can undergo chemical reactions with light do not efficiently absorb the light themselves. They rely on photocatalysts - materials that absorb light efficiently and then pass the energy on to the molecules to drive reactions.
In the new study, researchers have investigated an artificial photocatalyst material using nanoparticles and found out how to make it more efficient.
This could lead to better solar panels, as the energy from the Sun could be more efficiently harvested. The photocatalyst could also be used to destroy liquid or gas pollutants, such as pesticides in water, by harnessing sunlight to drive reactions that break down the chemicals into less harmful forms.
Lead author Dr Emiliano CortÚs from the Department of Physics at Imperial, said: "This finding opens new opportunities for increasing the efficiency of using and storing sunlight in various technologies. "By using these materials we can revolutionize our current capabilities for storing and using sunlight with important implications in energy conversion, as well as new uses such as destroying pollutant molecules or gases and water cleaning, among others."
The material that the team investigated is made of metal nanoparticles -- particles only billionths of a metre in diameter. Their results are published today in the Journal Nature Communications.
The team, which included researchers from the Chemistry Department at University of Duisburg-Essen in Germany led by Professor Sebastian SchlŘcker and theoreticians from the Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute and Harvard University at the US, showed that light-induced chemical reactions occur in certain regions over the surface of these nanomaterials.
They identified which areas of the nanomaterial would be most suitable for transferring energy to chemical reactions, by tracking the locations of very small gold nanoparticles (used as a markers) on the surface of the silver nanocatalytic material.
Now that they know which regions are responsible for the process of harvesting light and transferring it to chemical reactions, the team hope to be able to engineer the nanomaterial to increase these areas and make it more efficient.
Lead researcher Professor Stefan Maier said: "This is a powerful demonstration of how metallic nanostructures, which we have investigated in my group at Imperial for the last ten years, continue to surprise us in their abilities to control light on the nanoscale.
"The new finding uncovered by Dr CortÚs and his collaborators in Germany and the US opens up new possibilities for this field in the areas photocatalysis and nanochemistry."
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Hayley Dunning
020-759-42412
Copyright © Imperial College London
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
Chemistry
![]() Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
![]() Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








