Home > Press > Perovskite edges can be tuned for optoelectronic performance: Layered 2D material improves efficiency for solar cells and LEDs
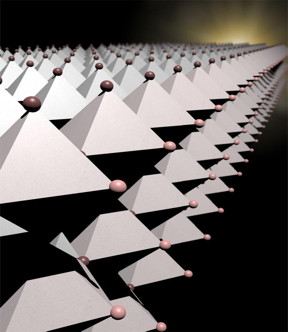 |
| Scientists at Los Alamos National Laboratory and their research partners are creating innovative 2-D layered hybrid perovskites that allow greater freedom in designing and fabricating efficient optoelectronic devices. CREDIT Los Alamos National Laboratory |
Abstract:
In the eternal search for next generation high-efficiency solar cells and LEDs, scientists at Los Alamos National Laboratory and their partners are creating innovative 2D layered hybrid perovskites that allow greater freedom in designing and fabricating efficient optoelectronic devices. Industrial and consumer applications could include low cost solar cells, LEDs, laser diodes, detectors, and other nano-optoelectronic devices.
Perovskite edges can be tuned for optoelectronic performance: Layered 2D material improves efficiency for solar cells and LEDs
Los Alamos, NM | Posted on March 10th, 2017"Our material is a layered compound, meaning it is a stack of 2D layers of perovskites with nanometer thickness (like a stack of sheets), and the 2D perovskite layers are separated by thin organic layers," said Jean-Christophe Blancon, lead author on a paper out today in the journal Science's First Release distribution. "This work could overturn conventional wisdom on the limitations of device designs based on layered perovskites."
The 2D, near-single-crystalline "Ruddlesden-Popper" thin films have an out-of-plane orientation so that uninhibited charge transport occurs through the perovskite layers in planar devices. At the edges of the perovskite layers, the new research discovered "layer-edge-states," which are key to both high efficiency of solar cells (>12 percent) and high fluorescence efficiency (a few tens of percent) for LEDs. The spontaneous conversion of excitons (bound electron-hole pairs) to free carriers via these layer-edge states appears to be the key to improving the photovoltaic and light-emitting thin-film layered materials.
The team investigated both photophysical and optoelectronic properties of phase-pure homogenous 2D perovskites. They were able to show that thin films have an intrinsic mechanism for dissociation of the strongly bound electron-hole pairs (excitons) to long-lived free-carriers provided by lower energy states at the edges of the layered perovskites.
Moreover, once carriers are trapped in these edge states, they remain protected and do not lose their energy via non-radiative processes. They can contribute to photocurrent in a photovoltaic (PV) device or radiatively recombine efficiently for light-emission applications. "These materials are quantum hybrid materials, possessing physical properties of both organic semiconductors and inorganic semiconducting quantum wells. We are just beginning to understand the interplay of the organic and inorganic components in 2D perovskites and this result underpins how unique properties can arise from competing physical properties," said Jared Crochet of the Physical Chemistry and Applied Spectroscopy group at Los Alamos.
"These results address a long-standing problem not just for the perovskite family, but relevant to a large group of materials where edges and surface states generally degrade the optoelectronic properties, which can now be chemically designed and engineered to achieve efficient flow of charge and energy leading to high-efficiency optoelectronic devices," said Aditya Mohite, who leads the perovskite program in the Material Synthesis and Integrated devices group at Los Alamos.
"The 2D hybrid perovskites continue to surprise. When we first designed these materials we were hoping that high quality samples of them would exhibit novel optoelectronic properties," said co-author Mercouri Kanatzidis of Northwestern University. "Well, they have done so and then some. They have exceeded our expectations and are proving to be truly amazing systems. We have only scratched the surface of what is there--sorry for the pun--in this 2D family and we anticipate continued excitement going forward."
unding: The work at Los Alamos National Laboratory was supported by the Laboratory Directed Research and Development program and was partially performed at the Center for Nonlinear Studies. The work was conducted, in part, at the Center for Integrated Nanotechnologies (CINT), a U.S. Department of Energy, Office of Science user facility. Work at Northwestern University was supported by grant SC0012541 from the U.S. Department of Energy, Office of Science. The work in France was supported by Cellule Energie du CNRS (SOLHYBTRANS Project) and University of Rennes 1 (Action Incitative, Défis Scientifique Emergents 2015). This research used resources of the Center for Functional Nanomaterials, which is a U.S. DOE Office of Science Facility, at Brookhaven National Laboratory under Contract No. DE-SC0012704.
####
About Los Alamos National Laboratory
Los Alamos National Laboratory, a multidisciplinary research institution engaged in strategic science on behalf of national security, is operated by Los Alamos National Security, LLC, a team composed of Bechtel National, the University of California, BWX Technologies, Inc. and URS Corporation for the Department of Energy's National Nuclear Security Administration.
Los Alamos enhances national security by ensuring the safety and reliability of the U.S. nuclear stockpile, developing technologies to reduce threats from weapons of mass destruction, and solving problems related to energy, environment, infrastructure, health and global security concerns.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Nancy Ambrosiano
505-667-0471
Copyright © Los Alamos National Laboratory
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
2 Dimensional Materials
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Display technology/LEDs/SS Lighting/OLEDs
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Perovskites
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
![]() Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








