Home > Press > Researchers optimize the assembly of micro-/meso-/macroporous carbon for Li-S batteries
 |
Abstract:
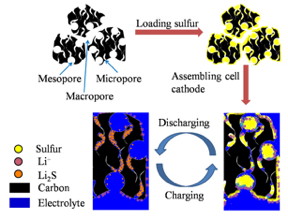
Li-S batteries are considered as promising alternatives for Li-ion batteries in the new generation of energy storages, due to high specific capacity (1675 mAh/g) and energy density (2600 mWh/g) of sulfur. But the poor conductivity of sulfur and severe shuttle effect of reaction intermediates destory the stability of this system. A variety of porous carbon materials have been applied as sulfur host to improve the performances of Li-S batteries for high conductivity, specific surface area and absorption effect. However, what kind of porous carbon would be the optimal choice to accommodate active material? And Which characteristic of carbon pores should be emphasized? A team of researchers from the School of Materials Science and Engineering and School of Electronic Science and Applied Physics at Hefei University of Technology demostrated that pore size distribution substantially influences the performances of cathode rather than specific surface area and total pore volume. Furthermore, an optimized assembly of micro/meso/macroporous carbon enables cathode present greatly improved electrochemical performances, in which micropore-volume-ratio to the total pore volume dominates cycling stability of batteries, meso/macropore-volume-ratio influences spaces for sulfur loading and channels to ion transfer. This research provides a direction of fabricating porous materials for energy storage.The report appears in the latest issue of the journal NANO.
Researchers optimize the assembly of micro-/meso-/macroporous carbon for Li-S batteries
Singapore | Posted on February 13th, 2017Based on the traditional S/C cathode, the effects of surface area, total pore volume and pore size distribution of carbon pores on performances of Li-S batteries are compared. In addition, on the premise of identically high sulfur content, the relation of the micro/meso/macropore volume ratio with the capacity, voltage plateau, rate capability, and cycle stability of Li-S battery are investigated. Among the samples, the porous carbon possesses the largest micropore volume ratio of 47.54% while a medium specific surface area of 1217 m2/g and inferior total pore volume of 0.54 cm3/g presents the highest initial discharge specific capacity of 1327 mAh/g and retention of 630 mAh/g over 100 cycles at 0.2C rate along with the best rate capability. The conclusions in this study can be directly applied in material fabrication for other systems of energy storage and even as criterions for further modification of Li-S batteries based on carbon material.
This research was supported by the "Strategic Priority Research Program" of the Chinese Academy of Science (NO. XDA03040000) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (NO. 103-4115100010) of China.
####
About World Scientific
World Scientific Publishing is a leading independent publisher of books and journals for the scholarly, research, professional and educational communities. The company publishes about 600 books annually and about 130 journals in various fields. World Scientific collaborates with prestigious organisations like the Nobel Foundation, US National Academies Press, as well as its subsidiary, the Imperial College Press, amongst others, to bring high quality academic and professional content to researchers and academics worldwide. To find out more about World Scientific, please visit www.worldscientific.com.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Chin Wanying
656-466-5775
Copyright © World Scientific
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








