Home > Press > New laser based on unusual physics phenomenon could improve telecommunications, computing
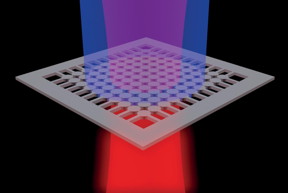 |
| This is a schematic of the BIC laser: a high frequency laser beam (blue) powers the membrane to emit a laser beam at telecommunication frequency (red). CREDIT Kanté group, UC San Diego |
Abstract:
Researchers at the University of California San Diego have demonstrated the world's first laser based on an unconventional wave physics phenomenon called bound states in the continuum. The technology could revolutionize the development of surface lasers, making them more compact and energy-efficient for communications and computing applications. The new BIC lasers could also be developed as high-power lasers for industrial and defense applications.
New laser based on unusual physics phenomenon could improve telecommunications, computing
San Diego, CA | Posted on January 12th, 2017"Lasers are ubiquitous in the present day world, from simple everyday laser pointers to complex laser interferometers used to detect gravitational waves. Our current research will impact many areas of laser applications," said Ashok Kodigala, an electrical engineering Ph.D. student at UC San Diego and first author of the study.
"Because they are unconventional, BIC lasers offer unique and unprecedented properties that haven't yet been realized with existing laser technologies," said Boubacar Kanté, electrical engineering professor at the UC San Diego Jacobs School of Engineering who led the research.
For example, BIC lasers can be readily tuned to emit beams of different wavelengths, a useful feature for medical lasers made to precisely target cancer cells without damaging normal tissue. BIC lasers can also be made to emit beams with specially engineered shapes (spiral, donut or bell curve) -- called vector beams -- which could enable increasingly powerful computers and optical communication systems that can carry up to 10 times more information than existing ones.
"Light sources are key components of optical data communications technology in cell phones, computers and astronomy, for example. In this work, we present a new kind of light source that is more efficient than what's available today in terms of power consumption and speed," said Babak Bahari, an electrical engineering Ph.D. student in Kanté's lab and a co-author of the study.
Bound states in the continuum (BICs) are phenomena that have been predicted to exist since 1929. BICs are waves that remain perfectly confined, or bound, in an open system. Conventional waves in an open system escape, but BICs defy this norm -- they stay localized and do not escape despite having open pathways to do so.
In a previous study, Kanté and his team demonstrated, at microwave frequencies, that BICs could be used to efficiently trap and store light to enable strong light-matter interaction. Now, they're harnessing BICs to demonstrate new types of lasers. The team published the work Jan. 12 in Nature.
Making the BIC laser
The BIC laser in this work is constructed from a thin semiconductor membrane made of indium, gallium, arsenic and phosphorus. The membrane is structured as an array of nano-sized cylinders suspended in air. The cylinders are interconnected by a network of supporting bridges, which provide mechanical stability to the device.
By powering the membrane with a high frequency laser beam, researchers induced the BIC system to emit its own lower frequency laser beam (at telecommunication frequency).
"Right now, this is a proof of concept demonstration that we can indeed achieve lasing action with BICs," Kanté said.
"And what's remarkable is that we can get surface lasing to occur with arrays as small as 8 × 8 particles," he said. In comparison, the surface lasers that are widely used in data communications and high-precision sensing, called VCSELs (vertical-cavity surface-emitting lasers), need much larger (100 times) arrays -- and thus more power -- to achieve lasing.
"The popular VCSEL may one day be replaced by what we're calling the 'BICSEL' -- bound state in the continuum surface-emitting laser, which could lead to smaller devices that consume less power," Kanté said. The team has filed a patent for the new type of light source.
The array can also be scaled up in size to create high power lasers for industrial and defense applications, he noted. "A fundamental challenge in high power lasers is heating and with the predicted efficiencies of our BIC lasers, a new era of laser technologies may become possible," Kanté said.
The team's next step is to make BIC lasers that are electrically powered, rather than optically powered by another laser. "An electrically pumped laser is easily portable outside the lab and can run off a conventional battery source," Kanté said.
This research was supported by a National Science Foundation Career Award (ECCS-1554021), the Office of Naval Research Multi-University Research Initiative (N000014-13-1-0678) and UC San Diego.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Liezel Labios
858-246-1124
Copyright © University of California, San Diego
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Wireless/telecommunications/RF/Antennas/Microwaves
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Optical computing/Photonic computing
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
![]() Nanophotonic platform boosts efficiency of nonlinear-optical quantum teleportation April 25th, 2025
Nanophotonic platform boosts efficiency of nonlinear-optical quantum teleportation April 25th, 2025
![]() Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
Industrial
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Quantum interference in molecule-surface collisions February 28th, 2025
Quantum interference in molecule-surface collisions February 28th, 2025
![]() Boron nitride nanotube fibers get real: Rice lab creates first heat-tolerant, stable fibers from wet-spinning process June 24th, 2022
Boron nitride nanotube fibers get real: Rice lab creates first heat-tolerant, stable fibers from wet-spinning process June 24th, 2022
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








