Home > Press > Construction of practical quantum computers radically simplified: Scientists invent ground-breaking new method that puts quantum computers within reach
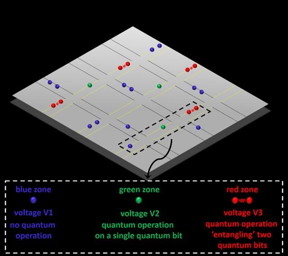 |
| A trapped-ion quantum computer would consist of an array of X-junctions with quantum bits formed by individual ions that are trapped above the surface of the quantum chip (shown in grey). Individual quantum bits are manipulated simply by tuning voltages as easy as tuning a radio to different stations. Applying voltage V1 results in no quantum operation (blue zones), applying voltage V2 results in a quantum operation on a single quantum bit (green zones), applying voltage V3 results in a quantum operation 'entangling' two quantum bits (red zones). An arbitrary large quantum computer can be constructed based on this simple-to engineer approach. CREDIT University of Sussex |
Abstract:
Scientists at the University of Sussex have invented a ground-breaking new method that puts the construction of large-scale quantum computers within reach of current technology.
Construction of practical quantum computers radically simplified: Scientists invent ground-breaking new method that puts quantum computers within reach
Brighton, UK | Posted on December 5th, 2016Quantum computers could solve certain problems - that would take the fastest supercomputer millions of years to calculate - in just a few milliseconds. They have the potential to create new materials and medicines, as well as solve long-standing scientific and financial problems.
Universal quantum computers can be built in principle - but the technology challenges are tremendous. The engineering required to build one is considered more difficult than manned space travel to Mars - until now.
Quantum computing on a small scale using trapped ions (charged atoms) is carried out by aligning individual laser beams onto individual ions with each ion forming a quantum bit. However, a large-scale quantum computer would need billions of quantum bits, therefore requiring billions of precisely aligned lasers, one for each ion.
Instead, scientists at Sussex have invented a simple method where voltages are applied to a quantum computer microchip (without having to align laser beams) - to the same effect.
Professor Winfried Hensinger and his team also succeeded in demonstrating the core building block of this new method with an impressively low error rate at their quantum computing facility at Sussex.
Professor Hensinger said: "This development is a game changer for quantum computing making it accessible for industrial and government use. We will construct a large-scale quantum computer at Sussex making full use of this exciting new technology."
Quantum computers may revolutionise society in a similar way as the emergence of classical computers. Dr Seb Weidt, part of the Ion Quantum Technology Group said: "Developing this step-changing new technology has been a great adventure and it is absolutely amazing observing it actually work in the laboratory."
The Ion Quantum Technology Group forms part of UK's National Quantum Technology Programme, a £270M investment by the UK Government to accelerate the translation of quantum technologies into the marketplace.
Prof. Hensinger heads the Ion Quantum Technology Group at the University of Sussex and he is Director of the Sussex Centre for Quantum Technologies. The group is part of the UK Quantum Technology Hub on Networked Quantum Information Technologies which is funded by the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC). As the main funding agency for engineering and physical sciences research, their vision is for the UK to be the best place in the world to Research, Discover and Innovate.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Julia Harris
Press Office
01-273-678-111
Copyright © University of Sussex
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Quantum Computing
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








