Home > Press > Bumpy surfaces, graphene beat the heat in devices: Rice University theory shows way to enhance heat sinks in future microelectronics
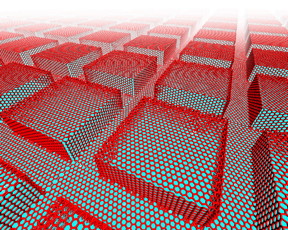 |
| Rice University researchers used computer models to determine the best way to disperse heat produced by microelectronic devices using gallium nitride semiconductors and diamond. A patterned surface and a layer of atom-thick graphene helped transport phonons from the semiconductor to the heat sink. Credit: Lei Tao/Rice University |
Abstract:
Bumpy surfaces with graphene between would help dissipate heat in next-generation microelectronic devices, according to Rice University scientists.
Bumpy surfaces, graphene beat the heat in devices: Rice University theory shows way to enhance heat sinks in future microelectronics
Houston, TX | Posted on November 29th, 2016Their theoretical studies show that enhancing the interface between gallium nitride semiconductors and diamond heat sinks would allow phonons – quasiparticles of sound that also carry heat – to disperse more efficiently. Heat sinks are used to carry heat away from electronic devices.
Rice computer models replaced the flat interface between the materials with a nanostructured pattern and added a layer of graphene, the atom-thick form of carbon, as a way to dramatically improve heat transfer, said Rice materials scientist Rouzbeh Shahsavari.
The new work by Shahsavari, Rice graduate student and lead author Lei Tao and postdoctoral researcher Sreeprasad Sreenivasan appeared this month in the American Chemical Society journal ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces.
No matter the size, electronic devices need to disperse the heat they produce, Shahsavari said. "With the current trend of constant increases in power and device miniaturization, efficient heat management has become a serious issue for reliability and performance," he said. "Oftentimes, the individual materials in hybrid nano- and microelectronic devices function well but the interface of different materials is the bottleneck for heat diffusion."
Gallium nitride has become a strong candidate for use in high-power, high-temperature applications like uninterruptible power supplies, motors, solar converters and hybrid vehicles, he said. Diamond is an excellent heat sink, but its atomic interface with gallium nitride is hard for phonons to traverse.
The researchers simulated 48 distinct grid patterns with square or round graphene pillars and tuned them to match phonon vibration frequencies between the materials. Sinking a dense pattern of small squares into the diamond showed a dramatic decrease in thermal boundary resistance of up to 80 percent. A layer of graphene between the materials further reduced resistance by 33 percent.
Fine-tuning the pillar length, size, shape, hierarchy, density and order will be important, Lei said.
"With current and emerging advancements in nanofabrication like nanolithography, it is now possible to go beyond the conventional planer interfaces and create strategically patterned interfaces coated with nanomaterials to significantly boost heat transport," Shahsavari said. "Our strategy is amenable to several other hybrid materials and provides novel insights to overcome the thermal boundary resistance bottleneck."
Shahsavari is an assistant professor of civil and environmental engineering and of materials science and nanoengineering.
The researchers used the Blue Gene supercomputer and the National Science Foundation-supported DAVinCI supercomputer, which are both administered by Rice’s Center for Research Computing and were procured in partnership with Rice’s Ken Kennedy Institute for Information Technology.
####
About Rice University
Located on a 300-acre forested campus in Houston, Rice University is consistently ranked among the nation’s top 20 universities by U.S. News & World Report. Rice has highly respected schools of Architecture, Business, Continuing Studies, Engineering, Humanities, Music, Natural Sciences and Social Sciences and is home to the Baker Institute for Public Policy. With 3,910 undergraduates and 2,809 graduate students, Rice’s undergraduate student-to-faculty ratio is 6-to-1. Its residential college system builds close-knit communities and lifelong friendships, just one reason why Rice is ranked No. 1 for happiest students and for lots of race/class interaction by the Princeton Review. Rice is also rated as a best value among private universities by Kiplinger’s Personal Finance. To read “What they’re saying about Rice,” go to http://tinyurl.com/RiceUniversityoverview .
Follow Rice News and Media Relations via Twitter @RiceUNews
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Jeff Falk
713-348-6775
Mike Williams
713-348-6728
Copyright © Rice University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Multiscale Materials Laboratory home page:
Multiscale Materials Laboratory home page:
![]() George R. Brown School of Engineering:
George R. Brown School of Engineering:
![]() Rice Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering:
Rice Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering:
![]() Rice Department of Materials Science and NanoEngineering:
Rice Department of Materials Science and NanoEngineering:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Hardware
![]() The present and future of computing get a boost from new research July 21st, 2023
The present and future of computing get a boost from new research July 21st, 2023
![]() A Carbon Nanotube Microprocessor Mature Enough to Say Hello: Three new breakthroughs make commercial nanotube processors possible March 2nd, 2020
A Carbon Nanotube Microprocessor Mature Enough to Say Hello: Three new breakthroughs make commercial nanotube processors possible March 2nd, 2020
![]() Powering the future: Smallest all-digital circuit opens doors to 5 nm next-gen semiconductor February 11th, 2020
Powering the future: Smallest all-digital circuit opens doors to 5 nm next-gen semiconductor February 11th, 2020
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Printing/Lithography/Inkjet/Inks/Bio-printing/Dyes
![]() Presenting: Ultrasound-based printing of 3D materials—potentially inside the body December 8th, 2023
Presenting: Ultrasound-based printing of 3D materials—potentially inside the body December 8th, 2023
![]() Simple ballpoint pen can write custom LEDs August 11th, 2023
Simple ballpoint pen can write custom LEDs August 11th, 2023
![]() Disposable electronics on a simple sheet of paper October 7th, 2022
Disposable electronics on a simple sheet of paper October 7th, 2022
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








