Home > Press > Researchers nearly reached quantum limit with nanodrums: Extremely accurate measurements of microwave signals can potentially be used for data encryption based on quantum cryptography and other purposes
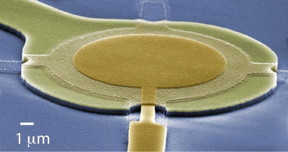 |
| Micro drums enable a nearly noiseless measurement of radio signals. The drum is made of thin superconducting aluminium film on top of a quartz chip (blue background). CREDIT Mika Sillanpää |
Abstract:
Researchers at Aalto University and the University of Jyväskylä have developed a new method of measuring microwave signals extremely accurately. This method can be used for processing quantum information, for example by efficiently transforming signals from microwave circuits to the optical regime.
Researchers nearly reached quantum limit with nanodrums: Extremely accurate measurements of microwave signals can potentially be used for data encryption based on quantum cryptography and other purposes
Aalto, Finland | Posted on November 2nd, 2016Important quantum limit
If you are trying to tune in a radio station but the tower is too far away, the signal gets distorted by noise. The noise results mostly from having to amplify the information carried by the signal in order to transfer it into an audible form. According to the laws of quantum mechanics, all amplifiers add noise. In the early 1980s, US physicist Carlton Caves proved theoretically that the Heisenberg uncertainty principle for such signals requires that at least half an energy quantum of noise must be added to the signal. In everyday life, this kind of noise does not matter, but researchers around the world have aimed to create amplifiers that would come close to Caves' limit.
'The quantum limit of amplifiers is essential for measuring delicate quantum signals, such as those generated in quantum computing or quantum mechanical measuring, because the added noise limits the size of signals that can be measured', explains Professor Mika Sillanpää.
From quantum bits to flying qubits
So far, the solution for getting closest to the limit is an amplifier based on superconducting tunnel junctions developed in the 1980s, but this technology has its problems. Led by Sillanpää, the researchers from Aalto and the University of Jyväskylä combined a nanomechanical resonator - a vibrating nanodrum - with two superconducting circuits, i.e. cavities.
'As a result, we have made the most accurate microwave measurement with nanodrums so far', explains Caspar Ockeloen-Korppi from Aalto University, who conducted the actual measurement.
In addition to the microwave measurement, this device enables transforming quantum information from one frequency to another while simultaneously amplifying it.
'This would for example allow transferring information from superconducting quantum bits to the "flying qubits" in the visible light range and back', envision the creators of the theory for the device, Tero Heikkilä, Professor at the University of Jyväskylä, and Academy Research Fellow Francesco Massel. Therefore, the method has potential for data encryption based on quantum mechanics, i.e. quantum cryptography, as well as other applications.
###
The research team also included researchers Juha-Matti Pirkkalainen and Erno Darmskägg from Aalto University. The work was published in Physical Review X, one of the most distinguished journals in physics, 28 October 2016. The work was conducted in the Center of Excellence on Low Temperature Quantum Phenomena and Devices in the Academy of Finland, and it was partially funded by the European Research Council.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Mika Sillanpää
358-503-447-330
Professor Tero Heikkilä
University of Jyväskylä
tel. +358 40 805 4804
Copyright © Aalto University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
Quantum Physics
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Quantum communication
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Quantum Computing
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Optical computing/Photonic computing
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
![]() Nanophotonic platform boosts efficiency of nonlinear-optical quantum teleportation April 25th, 2025
Nanophotonic platform boosts efficiency of nonlinear-optical quantum teleportation April 25th, 2025
![]() Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








