Home > Press > Hybrid nanostructures hold hydrogen well: Rice University scientists say boron nitride-graphene hybrid may be right for next-gen green cars
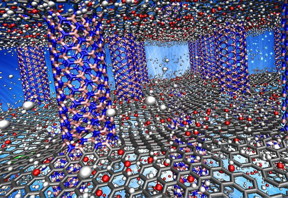 |
| Simulations by Rice University scientists show that pillared graphene boron nitride may be a suitable storage medium for hydrogen-powered vehicles. Above, the pink (boron) and blue (nitrogen) pillars serve as spacers for carbon graphene sheets (gray). The researchers showed the material worked best when doped with oxygen atoms (red), which enhanced its ability to adsorb and desorb hydrogen (white). CREDIT Lei Tao/Rice University |
Abstract:
Layers of graphene separated by nanotube pillars of boron nitride may be a suitable material to store hydrogen fuel in cars, according to Rice University scientists.
Hybrid nanostructures hold hydrogen well: Rice University scientists say boron nitride-graphene hybrid may be right for next-gen green cars
Houston, TX | Posted on October 25th, 2016The Department of Energy has set benchmarks for storage materials that would make hydrogen a practical fuel for light-duty vehicles. The Rice lab of materials scientist Rouzbeh Shahsavari determined in a new computational study that pillared boron nitride and graphene could be a candidate.
The study by Shahsavari and Farzaneh Shayeganfar appears in the American Chemical Society journal Langmuir.
Shahsavari's lab had already determined through computer models how tough and resilient pillared graphene structures would be, and later worked boron nitride nanotubes into the mix to model a unique three-dimensional architecture. (Samples of boron nitride nanotubes seamlessly bonded to graphene have been made.)
Just as pillars in a building make space between floors for people, pillars in boron nitride graphene make space for hydrogen atoms. The challenge is to make them enter and stay in sufficient numbers and exit upon demand.
In their latest molecular dynamics simulations, the researchers found that either pillared graphene or pillared boron nitride graphene would offer abundant surface area (about 2,547 square meters per gram) with good recyclable properties under ambient conditions. Their models showed adding oxygen or lithium to the materials would make them even better at binding hydrogen.
They focused the simulations on four variants: pillared structures of boron nitride or pillared boron nitride graphene doped with either oxygen or lithium. At room temperature and in ambient pressure, oxygen-doped boron nitride graphene proved the best, holding 11.6 percent of its weight in hydrogen (its gravimetric capacity) and about 60 grams per liter (its volumetric capacity); it easily beat competing technologies like porous boron nitride, metal oxide frameworks and carbon nanotubes.
At a chilly -321 degrees Fahrenheit, the material held 14.77 percent of its weight in hydrogen.
The Department of Energy's current target for economic storage media is the ability to store more than 5.5 percent of its weight and 40 grams per liter in hydrogen under moderate conditions. The ultimate targets are 7.5 weight percent and 70 grams per liter.
Shahsavari said hydrogen atoms adsorbed to the undoped pillared boron nitride graphene, thanks to weak van der Waals forces. When the material was doped with oxygen, the atoms bonded strongly with the hybrid and created a better surface for incoming hydrogen, which Shahsavari said would likely be delivered under pressure and would exit when pressure is released.
"Adding oxygen to the substrate gives us good bonding because of the nature of the charges and their interactions," he said. "Oxygen and hydrogen are known to have good chemical affinity."
He said the polarized nature of the boron nitride where it bonds with the graphene and the electron mobility of the graphene itself make the material highly tunable for applications.
"What we're looking for is the sweet spot," Shahsavari said, describing the ideal conditions as a balance between the material's surface area and weight, as well as the operating temperatures and pressures. "This is only practical through computational modeling, because we can test a lot of variations very quickly. It would take experimentalists months to do what takes us only days."
He said the structures should be robust enough to easily surpass the Department of Energy requirement that a hydrogen fuel tank be able to withstand 1,500 charge-discharge cycles.
###
Shayeganfar, a former visiting scholar at Rice, is an instructor at Shahid Rajaee Teacher Training University in Tehran, Iran. The researchers used the BlueBioU supercomputer and the National Science Foundation-supported DAVinCI supercomputer, which are both administered by Rice's Center for Research Computing and were procured in partnership with Rice's Ken Kennedy Institute for Information Technology.
####
About Rice University
Located on a 300-acre forested campus in Houston, Rice University is consistently ranked among the nation's top 20 universities by U.S. News & World Report. Rice has highly respected schools of Architecture, Business, Continuing Studies, Engineering, Humanities, Music, Natural Sciences and Social Sciences and is home to the Baker Institute for Public Policy. With 3,910 undergraduates and 2,809 graduate students, Rice's undergraduate student-to-faculty ratio is 6-to-1. Its residential college system builds close-knit communities and lifelong friendships, just one reason why Rice is ranked No. 1 for happiest students and for lots of race/class interaction by the Princeton Review. Rice is also rated as a best value among private universities by Kiplinger's Personal Finance. To read "What they're saying about Rice," go to tinyurl.com/RiceUniversityoverview.
Follow Rice News and Media Relations via Twitter @RiceUNews.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
David Ruth
713-348-6327
Mike Williams
713-348-6728
Copyright © Rice University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Multiscale Materials Laboratory home page:
Multiscale Materials Laboratory home page:
![]() George R. Brown School of Engineering:
George R. Brown School of Engineering:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanotubes/Buckyballs/Fullerenes/Nanorods/Nanostrings/Nanosheets
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Automotive/Transportation
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








