Home > Press > Smashing metallic cubes toughens them up: Rice University scientists fire micro-cubes at target to change their nanoscale structures
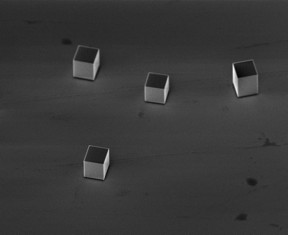 |
| Microscopic silver cubes were the bullets in Rice University experiments to show how deformation upon impact can make materials stronger and tougher. Credit: Thomas Group/Rice University |
Abstract:
Scientists at Rice University are smashing metallic micro-cubes to make them ultrastrong and tough by rearranging their nanostructures upon impact.
Smashing metallic cubes toughens them up: Rice University scientists fire micro-cubes at target to change their nanoscale structures
Houston, TX | Posted on October 20th, 2016The Rice team reported in Science this week that firing a tiny, nearly perfect cube of silver onto a hard target turns its single-crystal microstructure into a gradient-nano-grained (GNG) structure.
The purpose of the experiment was to learn how materials deform under overwhelming stress, as might be experienced by a bulletproof vest or a spacecraft that encounters micrometeorites. The researchers believe creating a gradient nanostructure in materials by way of deformation will make them more ductile and therefore less likely to fail catastrophically when subsequently stressed.
Ultimately, they want to develop nano-grained metals that are tougher and stronger than anything available today.
Led by materials scientist Edwin Thomas, the William and Stephanie Sick Dean of Rice's George R. Brown School of Engineering, the team used its advanced laser-induced projectile impact test (LIPIT) rig to shoot microcubes onto a silicon target. The mechanism allowed them to be sure the cube hit the target squarely.
The Thomas lab developed the LIPIT technique several years ago to fire microbullets to test the strength of polymer and graphene film materials. This time the researchers were essentially testing the bullet itself.
"The high-velocity impact generates very high pressure that far exceeds the material’s strength," Thomas said. "This leads to high plasticity at the impact side of the cube while the top region retains its initial structure, ultimately creating a grain-size gradient along its height."
The original projectiles needed to be as perfect as possible. That required a custom fabrication method, Thomas said. The cubes for the study were synthesized as single crystals via bottom-up seed growth to about 1.4 microns per side, about 50 times smaller than the width of a human hair.
LIPIT transformed laser power into the mechanical energy that propelled the cubes toward a target at supersonic velocity. The cubes were placed on top of a thin polymer film that thermally isolated them and prevented the laser itself from deforming them. When a laser pulse hit an absorbing thin-film gold layer underneath the polymer, the laser energy caused it to vaporize. That expanded the polymer film, which launched the microcubes.
The distance covered was small -- about 500 micrometers -- but the effect was large. While the experiments were carried out at room temperature, the cube's temperature rose by about 350 degrees Fahrenheit upon impact at 400 meters per second and allowed dynamic recrystallization.
The team fired silver cubes at the target at various orientations and measured the results of the impact from every angle, inside and out and from the nanoscale on up. Controlling the orientation of the crystal's impact gave them enormous ability to control the resulting structure and potentially its mechanical properties, Thomas said.
Other industrial processes produce materials with grains that can range from the nanocrystalline up to the coarse-grained, and, Thomas said, neither structure is ideal. While nanocrystalline structures make metals stronger, they also increase their susceptibility to catastrophic brittle failure due to the way those grains localize strain. Studies have demonstrated that creating a gradient-nano-grained structure from the nanometer to the micron scale may provide high strength yet alleviate such brittle failures by better distribution of stress.
The one-step Rice process makes such structures with a range of grains from about 10 to 500 nanometers over a distance of 500 nanometers. That produces a gradient at least 10 times higher than the other techniques, the researchers reported.
They also discovered the impact stores considerable elastic energy in the material, which leads to slow but continuous recrystallization of the metal at room temperature, even though silver’s melting point is more than 1,700 degrees Fahrenheit. Electron microscope analysis of samples eight days after impact showed the crystals were still seeking equilibrium, Thomas said.
In addition to promising pathways for creating ultrastrong and tough metals, the researchers believe their work may influence such other modern material processing techniques as cold spray and shot peening.
Rice postdoctoral researcher Ramathasan Thevamaran is lead author of the paper. Co-authors are Rice graduate student Olawale Lawal and research scientist Sadegh Yazdi and Rice alumni Seog-Jin Jeon, a postdoctoral researcher, and Jae-Hwang Lee, an assistant professor of mechanical and industrial engineering, both at the University of Massachusetts, Amherst.
####
About Rice University
Located on a 300-acre forested campus in Houston, Rice University is consistently ranked among the nation’s top 20 universities by U.S. News & World Report. Rice has highly respected schools of Architecture, Business, Continuing Studies, Engineering, Humanities, Music, Natural Sciences and Social Sciences and is home to the Baker Institute for Public Policy. With 3,910 undergraduates and 2,809 graduate students, Rice’s undergraduate student-to-faculty ratio is 6-to-1. Its residential college system builds close-knit communities and lifelong friendships, just one reason why Rice is ranked No. 1 for happiest students and for lots of race/class interaction by the Princeton Review. Rice is also rated as a best value among private universities by Kiplinger’s Personal Finance. To read “What they’re saying about Rice,” go to tinyurl.com/RiceUniversityoverview.
Follow Rice News and Media Relations via Twitter @RiceUNews.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
David Ruth
713-348-6327
Mike Williams
713-348-6728
Copyright © Rice University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
![]() NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
Plasmonics
![]() Unveiling the power of hot carriers in plasmonic nanostructures August 16th, 2024
Unveiling the power of hot carriers in plasmonic nanostructures August 16th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Aerospace/Space
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








