Home > Press > Towards the T-1000: Liquid metals propel future electronics: Self-propelling liquid metals a critical step to future elastic electronics
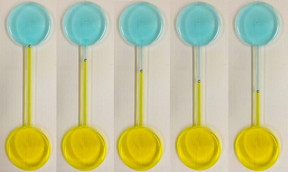 |
| Continuous motion of a self-propelling liquid metal droplet under a pH gradient, shown at different time intervals. The droplet is placed in a fluidic channel, midway between two reservoirs filled with different electrolytes of acidic and basic nature.
CREDIT: RMIT University |
Abstract:
Science fiction is inching closer to reality with the development of revolutionary self-propelling liquid metals -- a critical step towards future elastic electronics.
Towards the T-1000: Liquid metals propel future electronics: Self-propelling liquid metals a critical step to future elastic electronics
Melbourne, Australia | Posted on August 4th, 2016While building a shape-shifting liquid metal T-1000 Terminator may still be far on the horizon, the pioneering work by researchers at RMIT University in Melbourne, Australia, is setting the foundation for moving beyond solid state electronics towards flexible and dynamically reconfigurable soft circuit systems.
Watch the YouTube video: http://bit.ly/liquidmetalresearch
Modern electronic technologies like smart phones and computers are mainly based on circuits that use solid state components, with fixed metallic tracks and semiconducting devices.
But researchers dream of being able to create truly elastic electronic components -- soft circuit systems that can act more like live cells, moving around autonomously and communicating with each other to form new circuits rather than being stuck in one configuration.
Liquid metals, in particular non-toxic alloys of gallium, have so far offered the most promising path for realising that dream.
As well as being incredibly malleable, any droplet of liquid metal contains a highly-conductive metallic core and an atomically thin semiconducting oxide skin -- all the essentials needed for making electronic circuits.
To work out how to enable liquid metal to move autonomously, Professor Kourosh Kalantar-zadeh and his group from the School of Engineering at RMIT first immersed liquid metal droplets in water.
"Putting droplets in another liquid with an ionic content can be used for breaking symmetry across them and allow them to move about freely in three dimensions, but so far we have not understood the fundamentals of how liquid metal interacts with surrounding fluid," Kalantar-zadeh said.
"We adjusted the concentrations of acid, base and salt components in the water and investigated the effect.
"Simply tweaking the water's chemistry made the liquid metal droplets move and change shape, without any need for external mechanical, electronic or optical stimulants.
"Using this discovery, we were able to create moving objects, switches and pumps that could operate autonomously - self-propelling liquid metals driven by the composition of the surrounding fluid."
The research lays the foundation for being able to use "electronic" liquid metals to make 3D electronic displays and components on demand, and create makeshift and floating electronics.
"Eventually, using the fundamentals of this discovery, it may be possible to build a 3D liquid metal humanoid on demand - like the T-1000 Terminator but with better programming," Kalantar-zadeh said.
The research, which has potential applications in a range of industries including smart engineering solutions and biomedicine, is published on 4 August in Nature Communications.
In the paper, first author Dr Ali Zavabeti details the precise conditions in which liquid metals can be moved or stretched, how fluid on their surfaces moves around and -- as a result -- how they can make different flows.
The work also explains how the electric charges that accumulate on the surface of liquid metal droplets, together with their oxide skin, can be manipulated and used.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Kourosh Kalantar-zadeh
61-399-253-254
Copyright © RMIT University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Flexible Electronics
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() Flexible electronics integrated with paper-thin structure for use in space January 17th, 2025
Flexible electronics integrated with paper-thin structure for use in space January 17th, 2025
![]() Beyond wires: Bubble technology powers next-generation electronics:New laser-based bubble printing technique creates ultra-flexible liquid metal circuits November 8th, 2024
Beyond wires: Bubble technology powers next-generation electronics:New laser-based bubble printing technique creates ultra-flexible liquid metal circuits November 8th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








