Home > Press > New material could advance superconductivity
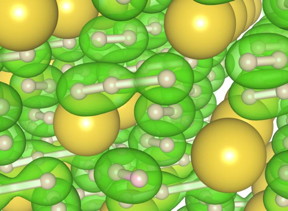 |
| At center, in green, is the new three-atom hydrogen 'chain.' It is surrounded by several 'normal' two-atom molecules of hydrogen, also in green. The new chain configuration appears in the new material NaH7, which was produced under high pressure and high temperature conditions. The new material could change the superconductivity landscape and be useful for hydrogen storage in hydrogen fuel cells.
Image courtesy Duck Young Kim |
Abstract:
Scientists have looked for different ways to force hydrogen into a metallic state for decades. A metallic state of hydrogen is a holy grail for materials science because it could be used for superconductors, materials that have no resistance to the flow of electrons, which increases electricity transfer efficiency many times over. For the first time researchers, led by Carnegie's Viktor Struzhkin, have experimentally produced a new class of materials blending hydrogen with sodium that could alter the superconductivity landscape and could be used for hydrogen-fuel cell storage. The research is published in Nature Communications.
New material could advance superconductivity
Washington, DC | Posted on July 31st, 2016It had been predicted that certain hydrogen-rich compounds consisting of multiple atoms of hydrogen with so-called alkali metals like lithium, potassium or sodium, could provide a new chemical means to alter the compound's electronic structure. This, in turn, may lead the way to metallic high-temperature superconductors.
"The challenge is temperature," explained Struzhkin. "The only superconductors that have been produced can only exist at impractically cold temperatures. In recent years, there have been predictions of compounds with several atoms of hydrogen coupled with alkali metals that could exist at more practical temperatures. They are theorized to have unique properties useful to superconductivity."
Now, the predictions have been confirmed. The Struzhkin team included Carnegie researchers Duck Young Kim, Elissaios Stavrou, Takaki Muramatsu, Ho-Kwang Mao, and Alexander Goncharov, with researchers from other institutions.*
The team used theory to guide their experiments and measured the samples using both a method that reveals the atomic structure (X-ray diffraction) and a method that identifies molecules by characteristics such as their minute vibrations and rotations (Raman spectroscopy). Theoretically, the sodium/hydrogen material would be stable under pressure, have metallic characteristics and unique structures, and show superconducting properties.
The team conducted high-pressure/high-temperature experiments. Matter under these extreme conditions can morph into new structures with new properties. They squeezed lithium and sodium samples in a diamond anvil cell to enormous pressures while heating the samples using a laser. At pressures between 300,000 and 400,000 atmospheres (30-40 gigapascals, or GPa) and temperatures of about 3100°F (2000 kelvin), they observed, for the first time, structures of "polyhydrides," sodium with 3 hydrogen atoms (NaH3) and NaH7--sodium with seven atoms of hydrogen--in very unusual configurations. Three negative charged hydrogen atoms in the NaH7 material lined up and looked like one-dimensional hydrogen chains, which is a new phase that is very different from pure hydrogen.
"This configuration was originally predicted to exist in 1972, more than 40 years ago," remarked Duck Young Kim. "It turns out that our experiments are in complete agreement with the theory, which predicted the existence of NaH3. The bonus is that we also observed the compound with seven hydrogen atoms."
Struzhkin reflected, "Further work needs to be done to see if materials in this class can be produced at lower temperatures and pressures. But this new class of matter opens up a whole new world of possibilities."
*Other researcher include Chris Pickard with the University College, London; Richard Needs of the Cavendish Laboratory in the UK; and Vitali Prakapenda of the University of Chicago. This work was supported by the DOE/BES; the Energy Frontier Research in Extreme Environments Center (EFree); the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC) of the UK; DARPA; and NSFC.
####
About Carnegie Institution for Science
The Carnegie Institution for Science is a private, nonprofit organization headquartered in Washington, D.C., with six research departments throughout the U.S. Since its founding in 1902, the Carnegie Institution has been a pioneering force in basic scientific research. Carnegie scientists are leaders in plant biology, developmental biology, astronomy, materials science, global ecology, and Earth and planetary science.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Viktor Struzhkin
Copyright © Carnegie Institution for Science
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Superconductivity
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() Lattice-driven charge density wave fluctuations far above the transition temperature in Kagome superconductor April 25th, 2025
Lattice-driven charge density wave fluctuations far above the transition temperature in Kagome superconductor April 25th, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








