Home > Press > Nanoscientists develop the 'ultimate discovery tool': Rapid discovery power is similar to what gene chips offer biology
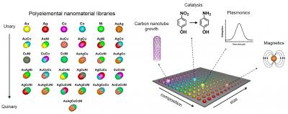 |
| A combinatorial library of polyelemental nanoparticles was developed using Dip-Pen Nanolithography. This novel nanoparticle library opens up a new field of nanocombinatorics for rapid screening of nanomaterials for a multitude of properties.
CREDIT: Peng-Cheng Chen/James Hedrick |
Abstract:
The discovery power of the gene chip is coming to nanotechnology. A Northwestern University research team is developing a tool to rapidly test millions and perhaps even billions or more different nanoparticles at one time to zero in on the best particle for a specific use.
Nanoscientists develop the 'ultimate discovery tool': Rapid discovery power is similar to what gene chips offer biology
Evanston, IL | Posted on June 25th, 2016When materials are miniaturized, their properties -- optical, structural, electrical, mechanical and chemical -- change, offering new possibilities. But determining what nanoparticle size and composition are best for a given application, such as catalysts, biodiagnostic labels, pharmaceuticals and electronic devices, is a daunting task.
"As scientists, we've only just begun to investigate what materials can be made on the nanoscale," said Northwestern's Chad A. Mirkin, a world leader in nanotechnology research and its application, who led the study. "Screening a million potentially useful nanoparticles, for example, could take several lifetimes. Once optimized, our tool will enable researchers to pick the winner much faster than conventional methods. We have the ultimate discovery tool."
Using a Northwestern technique that deposits materials on a surface, Mirkin and his team figured out how to make combinatorial libraries of nanoparticles in a very controlled way. (A combinatorial library is a collection of systematically varied structures encoded at specific sites on a surface.) Their study will be published June 24 by the journal Science.
The nanoparticle libraries are much like a gene chip, Mirkin says, where thousands of different spots of DNA are used to identify the presence of a disease or toxin. Thousands of reactions can be done simultaneously, providing results in just a few hours. Similarly, Mirkin and his team's libraries will enable scientists to rapidly make and screen millions to billions of nanoparticles of different compositions and sizes for desirable physical and chemical properties.
"The ability to make libraries of nanoparticles will open a new field of nanocombinatorics, where size -- on a scale that matters -- and composition become tunable parameters," Mirkin said. "This is a powerful approach to discovery science."
Mirkin is the George B. Rathmann Professor of Chemistry in the Weinberg College of Arts and Sciences and founding director of Northwestern's International Institute for Nanotechnology.
"I liken our combinatorial nanopatterning approach to providing a broad palette of bold colors to an artist who previously had been working with a handful of dull and pale black, white and grey pastels," said co-author Vinayak P. Dravid, the Abraham Harris Professor of Materials Science and Engineering in the McCormick School of Engineering.
Using five metallic elements -- gold, silver, cobalt, copper and nickel -- Mirkin and his team developed an array of unique structures by varying every elemental combination. In previous work, the researchers had shown that particle diameter also can be varied deliberately on the 1- to 100-nanometer length scale.
Some of the compositions can be found in nature, but more than half of them have never existed before on Earth. And when pictured using high-powered imaging techniques, the nanoparticles appear like an array of colorful Easter eggs, each compositional element contributing to the palette.
To build the combinatorial libraries, Mirkin and his team used Dip-Pen Nanolithography, a technique developed at Northwestern in 1999, to deposit onto a surface individual polymer "dots," each loaded with different metal salts of interest. The researchers then heated the polymer dots, reducing the salts to metal atoms and forming a single nanoparticle. The size of the polymer dot can be varied to change the size of the final nanoparticle.
This control of both size and composition of nanoparticles is very important, Mirkin stressed. Having demonstrated control, the researchers used the tool to systematically generate a library of 31 nanostructures using the five different metals.
To help analyze the complex elemental compositions and size/shape of the nanoparticles down to the sub-nanometer scale, the team turned to Dravid, Mirkin's longtime friend and collaborator. Dravid, founding director of Northwestern's NUANCE Center, contributed his expertise and the advanced electron microscopes of NUANCE to spatially map the compositional trajectories of the combinatorial nanoparticles.
Now, scientists can begin to study these nanoparticles as well as build other useful combinatorial libraries consisting of billions of structures that subtly differ in size and composition. These structures may become the next materials that power fuel cells, efficiently harvest solar energy and convert it into useful fuels, and catalyze reactions that take low-value feedstocks from the petroleum industry and turn them into high-value products useful in the chemical and pharmaceutical industries.
###
Mirkin is a member of the Robert H. Lurie Comprehensive Cancer Center of Northwestern University as well as co-director of the Northwestern University Center for Cancer Nanotechnology Excellence. He also is a professor of medicine, chemical and biological engineering, biomedical engineering and materials science at Northwestern.
The paper is titled "Polyelemental nanoparticle libraries." In addition to Mirkin and Dravid, authors of the paper are Peng-Cheng Chen (first author), Xiaolong Liu, James L. Hedrick, Zhuang Xie, Shunzhi Wang, Qing-Yuan Lin and Mark C. Hersam, all of Northwestern University.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Megan Fellman
847-491-3115
Copyright © Northwestern University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
Chemistry
![]() Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Fuel Cells
![]() Deciphering local microstrain-induced optimization of asymmetric Fe single atomic sites for efficient oxygen reduction August 8th, 2025
Deciphering local microstrain-induced optimization of asymmetric Fe single atomic sites for efficient oxygen reduction August 8th, 2025
![]() Current and Future Developments in Nanomaterials and Carbon Nanotubes: Applications of Nanomaterials in Energy Storage and Electronics October 28th, 2022
Current and Future Developments in Nanomaterials and Carbon Nanotubes: Applications of Nanomaterials in Energy Storage and Electronics October 28th, 2022
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
![]() Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Printing/Lithography/Inkjet/Inks/Bio-printing/Dyes
![]() Presenting: Ultrasound-based printing of 3D materials—potentially inside the body December 8th, 2023
Presenting: Ultrasound-based printing of 3D materials—potentially inside the body December 8th, 2023
![]() Simple ballpoint pen can write custom LEDs August 11th, 2023
Simple ballpoint pen can write custom LEDs August 11th, 2023
![]() Disposable electronics on a simple sheet of paper October 7th, 2022
Disposable electronics on a simple sheet of paper October 7th, 2022
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








