Home > Press > Rice University's nanosubs gain better fluorescent properties for tracking
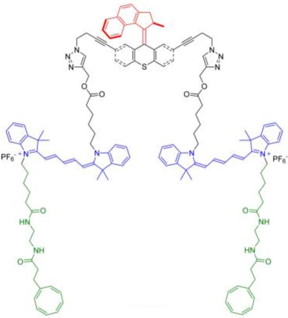 |
| Rice University scientists have created light-driven, single-molecule submersibles. A new version of the molecule strengthens its fluorescent response for better tracking. Atoms in red make up the light-activated motor. CREDIT: Tour Group/Rice University |
Abstract:
The next generation of nanosubmarines being developed at Rice University has been upgraded with tags that fluoresce longer, which enables the submersibles to be tracked for greater periods while being driven through a solution.
Rice University's nanosubs gain better fluorescent properties for tracking
Houston, TX | Posted on June 17th, 2016The single-molecule vehicles introduced by the Rice lab of chemist James Tour last year may someday be used to deliver drugs or other cargo. The new version built and tested with collaborators at Tel Aviv University in Israel is the subject of a recent paper in the American Chemical Society journal Organic Letters.
The first nanosub, USN-1, could be monitored but not imaged by a technique that would irradiate it with light for very short times. But that did not offer information about the submersible's trajectory, according to lead author Víctor García-Lopéz, a former Rice graduate student. The latest model, the 334-atom USN-2, can be viewed by single-molecule microscopy for at least 1.5 seconds, long enough for 30 frames of video.
"This makes it possible for us to track the trajectory of a single nanosubmersible," Tour said. "It should lead to a better understanding of how our vehicles move."
The lab attached cyclooctatetraene (COT) to the molecule's body and motor to keep them from bleaching, which quenches fluorescence. The light-driven motor developed by scientists in the Netherlands is a tail-like ligand that spins about a million times per second. The new subs, like the originals, are capable of moving 15 meters per second over nanoscale distances, based on the thrust provided by each turn of the rotating motor. Between the frequent collisions that stop their forward motion, Tour said, they are "the fastest-moving molecules ever seen in solution."
The nanosubmarines still can't be steered in the traditional sense, Tour said. The team is satisfied for the moment with achieving "enhanced diffusion" that lets them figure out how to move a one-molecule vehicle in a solution of similarly sized molecules.
"The next step is to track these nanosubmarines in solution and see if we can use them to deliver cargo or interact with cells," Tour said.
###
Co-authors are Rice visiting scholar Shunsuke Kuwahara of Toho University, Japan; Angel Martí, an associate professor of chemistry of bioengineering and of materials science and nanoengineering at Rice; and Jonathan Jeffet, a master's student, and Yuval Ebenstein, a senior lecturer in chemistry, at Tel Aviv University.
García-Lopéz is now a postdoctoral researcher at ETH Zurich in Switzerland. Tour is the T.T. and W.F. Chao Chair in Chemistry as well as a professor of computer science and of materials science and nanoengineering at Rice.
The National Science Foundation, the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan, the Yamada Science Foundation, the Israel Science Foundation and the European Research Councils supported the research.
####
About Rice University
Located on a 300-acre forested campus in Houston, Rice University is consistently ranked among the nation's top 20 universities by U.S. News & World Report. Rice has highly respected schools of Architecture, Business, Continuing Studies, Engineering, Humanities, Music, Natural Sciences and Social Sciences and is home to the Baker Institute for Public Policy. With 3,910 undergraduates and 2,809 graduate students, Rice's undergraduate student-to-faculty ratio is 6-to-1. Its residential college system builds close-knit communities and lifelong friendships, just one reason why Rice is ranked No. 1 for best quality of life and for lots of race/class interaction by the Princeton Review. Rice is also rated as a best value among private universities by Kiplinger's Personal Finance. To read "What they're saying about Rice," go to tinyurl.com/RiceUniversityoverview.
Follow Rice News and Media Relations via Twitter @RiceUNews.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
David Ruth
713-348-6327
Copyright © Rice University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Rice makes light-driven nanosubmarines:
Rice makes light-driven nanosubmarines:
![]() Wiess School of Natural Sciences:
Wiess School of Natural Sciences:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Molecular Machines
![]() First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
![]() Nanotech scientists create world's smallest origami bird March 17th, 2021
Nanotech scientists create world's smallest origami bird March 17th, 2021
![]() Giant nanomachine aids the immune system: Theoretical chemistry August 28th, 2020
Giant nanomachine aids the immune system: Theoretical chemistry August 28th, 2020
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








