Home > Press > Fast, stretchy circuits could yield new wave of wearable electronics
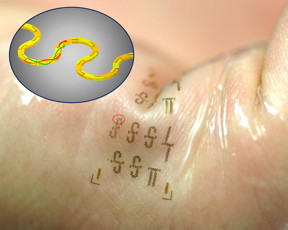 |
| Fabricated in interlocking segments like a 3-D puzzle, the new integrated circuits could be used in wearable electronics that adhere to the skin like temporary tattoos. Because the circuits increase wireless speed, these systems could allow health care staff to monitor patients remotely, without the use of cables and cords.
Image courtesy of Yei Hwan Jung and Juhwan Lee/University of Wisconsin-Madison |
Abstract:
The consumer marketplace is flooded with a lively assortment of smart wearable electronics that do everything from monitor vital signs, fitness or sun exposure to play music, charge other electronics or even purify the air around you -- all wirelessly.
Fast, stretchy circuits could yield new wave of wearable electronics
Madison, WI | Posted on May 30th, 2016Now, a team of University of Wisconsin-Madison engineers has created the world's fastest stretchable, wearable integrated circuits, an advance that could drive the Internet of Things and a much more connected, high-speed wireless world.
Led by Zhenqiang "Jack" Ma, the Lynn H. Matthias Professor in Engineering and Vilas Distinguished Achievement Professor in electrical and computer engineering at UW-Madison, the researchers published details of these powerful, highly efficient integrated circuits today, May 27, 2016, in the journal Advanced Functional Materials.
The advance is a platform for manufacturers seeking to expand the capabilities and applications of wearable electronics -- including those with biomedical applications -- particularly as they strive to develop devices that take advantage of a new generation of wireless broadband technologies referred to as 5G.
With wavelength sizes between a millimeter and a meter, microwave radio frequencies are electromagnetic waves that use frequencies in the .3 gigahertz to 300 gigahertz range. That falls directly in the 5G range.
In mobile communications, the wide microwave radio frequencies of 5G networks will accommodate a growing number of cellphone users and notable increases in data speeds and coverage areas.
In an intensive care unit, epidermal electronic systems (electronics that adhere to the skin like temporary tattoos) could allow health care staff to monitor patients remotely and wirelessly, increasing patient comfort by decreasing the customary tangle of cables and wires.
What makes the new, stretchable integrated circuits so powerful is their unique structure, inspired by twisted-pair telephone cables. They contain, essentially, two ultra-tiny intertwining power transmission lines in repeating S-curves.
This serpentine shape -- formed in two layers with segmented metal blocks, like a 3-D puzzle -- gives the transmission lines the ability to stretch without affecting their performance. It also helps shield the lines from outside interference and, at the same time, confine the electromagnetic waves flowing through them, almost completely eliminating current loss. Currently, the researchers' stretchable integrated circuits can operate at radio frequency levels up to 40 gigahertz.
And, unlike other stretchable transmission lines, whose widths can approach 640 micrometers (or .64 millimeters), the researchers' new stretchable integrated circuits are just 25 micrometers (or .025 millimeters) thick. That's tiny enough to be highly effective in epidermal electronic systems, among many other applications.
Ma's group has been developing what are known as transistor active devices for the past decade. This latest advance marries the researchers' expertise in both high-frequency and flexible electronics.
"We've found a way to integrate high-frequency active transistors into a useful circuit that can be wireless," says Ma, whose work was supported by the Air Force Office of Scientific Research. "This is a platform. This opens the door to lots of new capabilities."
###
Other authors on the paper include Yei Hwan Jung, Juhwan Lee, Namki Cho, Sang June Cho, Huilong Zhang, Subin Lee, Tong June Kim and Shaoqin Gong of UW-Madison and Yijie Qiu of the University of Electronic Science and Technology of China.
--Renee Meiller, , 608-262-2481
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Zhenqiang "Jack" Ma
608-261-1095
Copyright © University of Wisconsin-Madison
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Flexible Electronics
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() Flexible electronics integrated with paper-thin structure for use in space January 17th, 2025
Flexible electronics integrated with paper-thin structure for use in space January 17th, 2025
![]() Beyond wires: Bubble technology powers next-generation electronics:New laser-based bubble printing technique creates ultra-flexible liquid metal circuits November 8th, 2024
Beyond wires: Bubble technology powers next-generation electronics:New laser-based bubble printing technique creates ultra-flexible liquid metal circuits November 8th, 2024
Wearable electronics
![]() Breakthrough brings body-heat powered wearable devices closer to reality December 13th, 2024
Breakthrough brings body-heat powered wearable devices closer to reality December 13th, 2024
![]() Nanofibrous metal oxide semiconductor for sensory face November 8th, 2024
Nanofibrous metal oxide semiconductor for sensory face November 8th, 2024
![]() CityU awarded invention: Soft, ultrathin photonic material cools down wearable electronic devices June 30th, 2023
CityU awarded invention: Soft, ultrathin photonic material cools down wearable electronic devices June 30th, 2023
Internet-of-Things
![]() Nanofibrous metal oxide semiconductor for sensory face November 8th, 2024
Nanofibrous metal oxide semiconductor for sensory face November 8th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








