Home > Press > Magnetic vortices defy temperature fluctuations: Common magnetic mineral is reliable witness to Earth's history
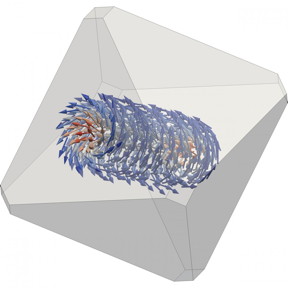 |
| This micromagnetic model shows the three-dimensional vortex structure of magnetite nanocrystals. CREDIT: University of Edinburgh |
Abstract:
Magnetic nanovortices in magnetite minerals are reliable witnesses of the earth's history, as revealed by the first high-resolution studies of these structures undertaken by scientists from Germany and the United Kingdom. The magnetic structures are built during the cooling of molten rock and reflect the earth's magnetic field at the time of their formation. The vortices are unexpectedly resilient to temperature fluctuations, as electron holographic experiments in Jülich have verified. These results are an important step in improving our understanding of the history of the earth's magnetic field, its core and plate tectonics. (Science Advances, DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.1501801)
Magnetic vortices defy temperature fluctuations: Common magnetic mineral is reliable witness to Earth's history
Juelich, Germany | Posted on April 19th, 2016The earth's magnetic field performs important functions: it protects us, for example, from charged particles from space and enables migratory birds, bees, and other animals to navigate. However, it is not stable, and constantly changes its intensity and state. Several times in the past it has even reversed its polarity - the north and south poles have changed places. Scientists in the area of paleomagnetism use magnetic minerals to investigate the history of the earth's magnetic field and its formation from molten metal flowing within the earth's core, the so-called geodynamo. Furthermore, the movement of continental plates can be monitored with the aid of such rocks.
In the course of millions of years, these minerals could often have been exposed to immense temperature fluctuations, due to extreme climate change or volcanic activity, for instance. How well do the magnetic structures survive such temperature fluctuations and how reliable is the information gained from them? An international research team has now studied this question for the first time at ultra-high resolution on samples of magnetite, the mineral dominating the magnetic properties in the earth's crust. "It is only in a small part of naturally occurring magnetite that magnetic structures known for being very stable with respect to temperature fluctuations are found," explains Dr. Trevor Almeida of Imperial College London. "Far more common are tiny magnetic vortices. Their stability could not be demonstrated until now."
Together with colleagues from Forschungszentrum Jülich, the University of Edinburgh and the University of Nottingham, Almeida has studied the magnetic vortices in magnetite nanocrystals. As the structures are so tiny - each grain is only about the size of a virus - there is only one method with which the nanovortices can directly be observed while they are heated up and cooled down: "A special high-resolution electron microscope at the Ernst Ruska-Centre (ER-C) in Jülich is capable of making magnetic fields on the nanoscale holographically visible," explains Almeida. "In this way, images of field lines are produced almost like using iron filings around a bar magnet to make its magnetic field visible, but with a resolution in the nanometre range."
The experiments in Jülich showed that although the magnetic vortices alter in strength and direction when heated up, they go back to their original state as they cool down. "Therefore magnetite rocks, which carry signs of temperature fluctuations, are indeed a reliable source of information about the history of the earth," enthuses Almeida.
"Electron holography has made it possible for us to gain a completely new insight into the magnetic behaviour of magnetite," emphasized Prof. Rafal Dunin-Borkowski, Director at the ER-C and at the Peter Grünberg Institute in Jülich. As an expert in electron holography, he works with his Jülich team on further improving the resolution of this technique and in providing German and international scientists the necessary infrastructure to perform this type of study. "Weak magnetic fields in nanocrystals don't just play a role in paleomagnetism. In information technology, for instance, electron holograms can also be of use to help to push back the physical limits of data storage and processing."
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Angela Wenzik
49-246-161-6048
Prof. Dr. Rafal Dunin-Borkowski
Ernst Ruska-Centre for Microscopy and Spectroscopy with Electrons
Peter Grünberg Institute
"Microstructure Research" (PGI-5)
Forschungszentrum Jülich
Tel. +49 2461 61-9297
Dr. Trevor Almeida
Natural Magnetism Group
Imperial College London & School of Physics and Astronomy
University of Glasgow
Tel. +44 141 330 2879
Copyright © Forschungszentrum Juelich
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
Magnetism/Magnons
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Memory Technology
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








