Home > Press > Riddle of missing efficiency in zinc oxide-based dye-sensitised solar cells solved
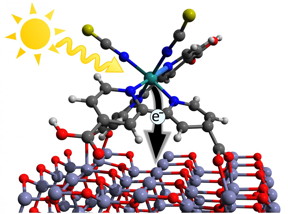 |
| Illustration of the initial charge transfer step in a dye sensitized solar cell. A photon from the sun is absorbed and excites the dye molecule. Subsequently, an electron can is injected into the ZnO-Layer where it can be trapped by so called interface-states. CREDIT: HZB/Mario Borgwardt |
Abstract:
This explains why zinc-oxide (ZnO) dye-sensitised solar cells have not yet met expectations. The results evolved from collaboration between Monash University (Australia) and Joint Lab partners Helmholtz Zentrum Berlin (HZB) and the Freie Universität Berlin (FU Berlin). They have now been published online by Nature in the open access magazine Scientific Reports.
Riddle of missing efficiency in zinc oxide-based dye-sensitised solar cells solved
Berlin, Germany | Posted on April 15th, 2016Converting the energy of the sun into electricity and solar hydrogen can be achieved with a whole series of materials. One important class of organic solar cells uses dyes applied to a semiconductor material like titanium dioxide (TiO2), for example. The dye molecules function as a kind of "translator" for the solar energy. They capture the light and inject electrons as free charges carriers into the TiO2 resulting in current flow. However, TiO2 is far from ideal and zinc oxide (ZnO) should actually be more suitable as an electrode material. This is because the charge carriers are far more mobile in ZnO, so they should flow more quickly after charge separation has occurred. In addition, nanostructures that capture sunlight especially efficiently can be produced in simple fashion using ZnO.
Detailed investigation of excited states with ultrashort Laser pulses
Nevertheless, constructing ZnO solar cells that better those of TiO2 had not been accomplished thus far. Now a team headed by Emad Aziz has for the first time directly observed the cause for this and investigated it in detail at the "Joint Ultrafast Dynamics Lab in Solutions and at Interfaces". The Joint Lab is being operated by HZB together with FU Berlin. It has a complete array of state-of-the-art laser instruments at its disposal, including a time-resolved photoelectron spectrometer that can generate ultra-short XUV pulses with duration below 45 femtoseconds. These ultra-short light pulses enable the temporal as well as energetic development of excited states to be tracked on ultra-short timescales.
Interface states as traps for charge carriers
"Our measurements show directly for the first time that charge carriers are temporarily trapped by formation of an interface state between the dye and the semiconductor boundary layer. As a result, they are no longer immediately available as free charge carriers", explains Mario Borgwardt, doctoral student on Aziz' team. These "trapped" electrons within the interface stay put longer. This increases the probability that they are "lost" again through recombination. That in turn reduces the efficiency level of the solar cell.
The samples for the experiment were made available by Prof. Leone Spiccia's team from Monash University, Australia. A fruitful collaboration evolved in the course of Spiccia's visit last year as part of his Helmholtz International Fellowship award from the Helmholtz Association that has contributed in a fundamental manner to the success of this project.
Helpful hints for the design of materials for energy conversion or storage
Aziz explains the importance of the results: "The work has led to a better understanding of the processes at the boundary layer between dye molecule and semiconductor. We have therefore been able to understand how dye and semiconductor materials communicate with one another. This enables us now to devise approaches for improving the communication in a direct way. That is important not only for the design of dye-sensitised solar cells, but also in order to be able to develop systems of materials for photocatalytic generation of hydrogen for storing solar energy as hydrogen fuel."
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Prof. Dr. Emad Aziz
49-308-062-15003
Copyright © Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin für Materialien und Energie (HZB)
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
![]() Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








