Home > Press > UCSB researchers identify specific defects in LED diodes that lead to less efficient solid state lighting
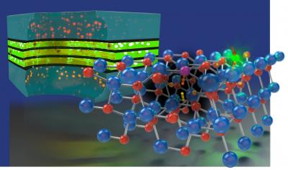 |
| A conceptual illustration of how defects in a crystal lattice might contribute to nonradiative recombination of electrons and holes in LEDs. CREDIT: Peter Allen/UCSB illustration |
Abstract:
Using state-of-the-art theoretical methods, UCSB researchers have identified a specific type of defect in the atomic structure of a light-emitting diode (LED) that results in less efficient performance. The characterization of these point defects could result in the fabrication of even more efficient, longer lasting LED lighting.
UCSB researchers identify specific defects in LED diodes that lead to less efficient solid state lighting
Santa Barbara, CA | Posted on April 9th, 2016"Techniques are available to assess whether such defects are present in the LED materials and they can be used to improve the quality of the material," said materials professor Chris Van de Walle, whose research group carried out the work.
In the world of high-efficiency solid-state lighting, not all LEDs are alike. As the technology is utilized in a more diverse array of applications -- including search and rescue, water purification and safety illumination, in addition to their many residential, industrial and decorative uses -- reliability and efficiency are top priorities. Performance, in turn, is heavily reliant on the quality of the semiconductor material at the atomic level.
"In an LED, electrons are injected from one side, holes from the other," explained Van de Walle. As they travel across the crystal lattice of the semiconductor -- in this case gallium-nitride-based material -- the meeting of electrons and holes (the absence of electrons) is what is responsible for the light that is emitted by the diode: As electron meets hole, it transitions to a lower state of energy, releasing a photon along the way.
Occasionally, however, the charge carriers meet and do not emit light, resulting in the so-called Shockley-Read-Hall (SRH) recombination. According to the researchers, the charge carriers are captured at defects in the lattice where they combine, but without emitting light.
The defects identified involve complexes of gallium vacancies with oxygen and hydrogen. "These defects had been previously observed in nitride semiconductors, but until now, their detrimental effects were not understood," explained lead author Cyrus Dreyer, who performed many of the calculations on the paper.
"It was the combination of the intuition that we have developed over many years of studying point defects with these new theoretical capabilities that enabled this breakthrough," said Van de Walle, who credits co-author Audrius Alkauskas with the development of a theoretical formalism necessary to calculate the rate at which defects capture electrons and holes.
The method lends itself to future work identifying other defects and mechanisms by which SRH recombination occurs, said Van de Walle.
"These gallium vacancy complexes are surely not the only defects that are detrimental," he said. "Now that we have the methodology in place, we are actively investigating other potential defects to assess their impact on nonradiative recombination."
###
This work was funded by U. S. Department of Energy Office of Science, and by Marie Sklodowska-Curie Action of the European Union.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Sonia Fernandez
805-893-4765
Copyright © University of California, Santa Barbara
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Display technology/LEDs/SS Lighting/OLEDs
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Efficient and stable hybrid perovskite-organic light-emitting diodes with external quantum efficiency exceeding 40 per cent July 5th, 2024
Efficient and stable hybrid perovskite-organic light-emitting diodes with external quantum efficiency exceeding 40 per cent July 5th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








