Home > Press > Lithium battery catalyst found to harm key soil microorganism
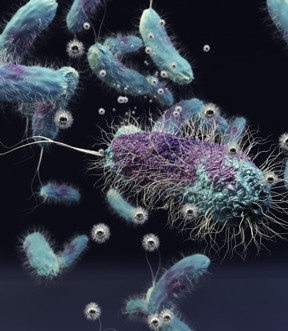 |
| Shewanella oneidensis is a ubiquitous, globally distributed soil bacterium. In nature, the microbe thrives on metal ions, converting them to metals like iron that serve as nutrients for other microbes. The bacterium was shown to be harmed by the compound nickel manganese cobalt oxide, which is produced in nanoparticle form and is the material poised to become the dominant material in the lithium ion batteries that will power portable electronics and electric vehicles.
Illustration: Ella Marushchenko/University of Minnesota |
Abstract:
The material at the heart of the lithium ion batteries that power electric vehicles, laptop computers and smartphones has been shown to impair a key soil bacterium, according to new research published online in the journal Chemistry of Materials.
Lithium battery catalyst found to harm key soil microorganism
Madison, WI | Posted on February 7th, 2016The study by researchers at the University of Wisconsin-Madison and the University of Minnesota is an early signal that the growing use of the new nanoscale materials used in the rechargeable batteries that power portable electronics and electric and hybrid vehicles may have untold environmental consequences.
Researchers led by UW-Madison chemistry Professor Robert J. Hamers explored the effects of the compound nickel manganese cobalt oxide (NMC), an emerging material manufactured in the form of nanoparticles that is being rapidly incorporated into lithium ion battery technology, on the common soil and sediment bacterium Shewanella oneidensis.
"As far as we know, this is the first study that's looked at the environmental impact of these materials," says Hamers, who collaborated with the laboratories of University of Minnesota chemist Christy Haynes and UW-Madison soil scientist Joel Pedersen to perform the new work.
NMC and other mixed metal oxides manufactured at the nanoscale are poised to become the dominant materials used to store energy for portable electronics and electric vehicles. The materials, notes Hamers, are cheap and effective.
"Nickel is dirt cheap. It's pretty good at energy storage. It is also toxic. So is cobalt," Hamers says of the components of the metal compound that, when made in the form of nanoparticles, becomes an efficient cathode material in a battery, and one that recharges much more efficiently than a conventional battery due to its nanoscale properties.
Hamers, Haynes and Pedersen tested the effects of NMC on a hardy soil bacterium known for its ability to convert metal ions to nutrients. Ubiquitous in the environment and found worldwide, Shewanella oneidensis, says Haynes, is "particularly relevant for studies of potentially metal-releasing engineered nanomaterials. You can imagine Shewanella both as a toxicity indicator species and as a potential bioremediator."
Subjected to the particles released by degrading NMC, the bacterium exhibited inhibited growth and respiration. "At the nanoscale, NMC dissolves incongruently," says Haynes, releasing more nickel and cobalt than manganese. "We want to dig into this further and figure out how these ions impact bacterial gene expression, but that work is still underway."
Haynes adds that "it is not reasonable to generalize the results from one bacterial strain to an entire ecosystem, but this may be the first 'red flag' that leads us to consider this more broadly."
The group, which conducted the study under the auspices of the National Science Foundation-funded Center for Sustainable Nanotechnology at UW-Madison, also plans to study the effects of NMC on higher organisms.
According to Hamers, the big challenge will be keeping old lithium ion batteries out of landfills, where they will ultimately break down and may release their constituent materials into the environment.
"There is a really good national infrastructure for recycling lead batteries," he says. "However, as we move toward these cheaper materials there is no longer a strong economic force for recycling. But even if the economic drivers are such that you can use these new engineered materials, the idea is to keep them out of the landfills. There is going to be 75 to 80 pounds of these mixed metal oxides in the cathodes of an electric vehicle."
Hamers argues that there are ways for industry to minimize the potential environmental effects of useful materials such as coatings, "the M&M strategy," but the ultimate goal is to design new environmentally benign materials that are just as technologically effective.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Robert J. Hamers
608-262-6371
Terry Devitt
(608) 262-8282
Robert J. Hamers
(608) 262-6371
Christy Haynes
(612) 626-1096
Copyright © University of Wisconsin-Madison
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Safety-Nanoparticles/Risk management
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
![]() Closing the gaps — MXene-coating filters can enhance performance and reusability February 28th, 2025
Closing the gaps — MXene-coating filters can enhance performance and reusability February 28th, 2025
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








