Home > Press > Quantum knots are real!
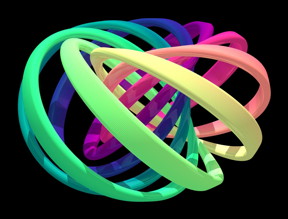 |
| Visualization of the structure of the created quantum knot. Each colorful band represents a set of nearby directions of the quantum field that is knotted. Note that each band is twisted and linked with the others once. Untying the knot requires the bands to separate, which is not possible without breaking them. CREDIT: David Hall |
Abstract:
The very first experimental observations of knots in quantum matter have just been reported in Nature Physics by scientists at Aalto University (Finland) and Amherst College (USA). The scientists created knotted solitary waves, or knot solitons, in the quantum-mechanical field describing a gas of superfluid atoms, also known as a Bose-Einstein condensate.
Quantum knots are real!
Aalto, Finland | Posted on January 20th, 2016In contrast to knotted ropes, the created quantum knots exist in a field that assumes a certain direction at every point of space. The field segregates into an infinite number of linked rings, each with its own field direction. The resulting structure is topologically stable as it cannot be separated without breaking the rings. In other words, one cannot untie the knot within the superfluid unless one destroys the state of the quantum matter.
To make this discovery we exposed a Rubidium condensate to rapid changes of a specifically tailored magnetic field, tying the knot in less than a thousandth of a second. After we learned how to tie the first quantum knot, we have become rather good at it. Thus far, we have tied several hundred such knots, says Professor David Hall, Amherst College.
The scientists tied the knot by squeezing the structure into the condensate from its outskirts. This required them to initialize the quantum field to point in a particular direction, after which they suddenly changed the applied magnetic field to bring an isolated null point, at which the magnetic field vanishes, into the center of the cloud. Then they just waited for less than a millisecond for the magnetic field to do its trick and tie the knot.
For decades, physicists have been theoretically predicting that it should be possible to have knots in quantum fields, but nobody else has been able to make one. Now that we have seen these exotic beasts, we are really excited to study their peculiar properties. Importantly, our discovery connects to a diverse set of research fields including cosmology, fusion power, and quantum computers, says research group leader Mikko Möttönen, Aalto University.
Knots have been used and appreciated by human civilizations for thousands of years. For example, they have enabled great seafaring expeditions and inspired intricate designs and patterns. The ancient Inca civilization used a system of knots known as quipu to store information. In modern times, knots have been thought to play important roles in the quantum-mechanical foundations of nature, although they have thus far remained unseen in quantum dynamics.
In everyday life, knots are typically tied on ropes or strings with two ends. However, these kinds of knots are not what mathematicians call topologically stable since they can be untied without cutting the rope. In stable knots, the ends of the ropes are glued together. Such knots can be relocated within the rope but cannot be untied without scissors.
Mathematically speaking, the created quantum knot realizes a mapping referred to as Hopf fibration that was discovered by Heinz Hopf in 1931. The Hopf fibration is still widely studied in physics and mathematics. Now it has been experimentally demonstrated for the first time in a quantum field.
This is the beginning of the story of quantum knots. It would be great to see even more sophisticated quantum knots to appear such as those with knotted cores. Also it would be important to create these knots in conditions where the state of the quantum matter would be inherently stable. Such system would allow for detailed studies of the stability of the knot itself, says Mikko Möttönen.
Funding
This material is based upon work supported by the National Science Foundation under Grant No. PHY-1205822, the Academy of Finland (grant nos. 251748, 284621, 135794, and 272806), Finnish Doctoral Programme in Computational Sciences, and the Magnus Ehrnrooth Foundation. Any opinions, findings, and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the views of the National Science Foundation.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Mikko Möttönen
Docent, Professor
358-50-594-0950 (Time zone: GMT +2)
Aalto University and University of Jyväskylä
http://physics.aalto.fi/en/groups/qcd/
Mikko Möttönen is the leader of the theoretical and computational part of the research. Theoretical insight and computational modelling was very important for the success of the creation of the knots. The modelling was carried out using the facilities at CSC -- IT Center for Science Ltd and at Aalto University (Aalto Science-IT project).
David S. Hall, Professor
Amherst College
1-413-542-2072 (Time zone: GMT -5)
http://www3.amherst.edu/~halllab/
David S. Hall is the leader of the experimental part of the research. The quantum knots were created in the Physics Laboratories at Amherst College, United States of America.
Copyright © Aalto University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() The research article (This article should be credited as the source of stories covered.)
The research article (This article should be credited as the source of stories covered.)
![]() The submitted version of the manuscript is openly available at:
The submitted version of the manuscript is openly available at:
| Related News Press |
Quantum Physics
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Videos/Movies
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








