Home > Press > UCLA researchers create exceptionally strong and lightweight new metal: Magnesium infused with dense silicon carbide nanoparticles could be used for airplanes, cars, mobile electronics and more
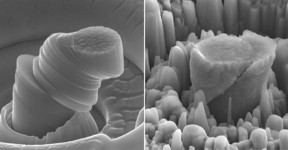 |
| At left, a deformed sample of pure metal; at right, the strong new metal made of magnesium with silicon carbide nanoparticles. Each central micropillar is about 4 micrometers across.
CREDIT: UCLA Scifacturing Laboratory |
Abstract:
A team led by researchers from the UCLA Henry Samueli School of Engineering and Applied Science has created a super-strong yet light structural metal with extremely high specific strength and modulus, or stiffness-to-weight ratio. The new metal is composed of magnesium infused with a dense and even dispersal of ceramic silicon carbide nanoparticles. It could be used to make lighter airplanes, spacecraft, and cars, helping to improve fuel efficiency, as well as in mobile electronics and biomedical devices.
UCLA researchers create exceptionally strong and lightweight new metal: Magnesium infused with dense silicon carbide nanoparticles could be used for airplanes, cars, mobile electronics and more
Los Angeles, CA | Posted on December 24th, 2015To create the super-strong but lightweight metal, the team found a new way to disperse and stabilize nanoparticles in molten metals. They also developed a scalable manufacturing method that could pave the way for more high-performance lightweight metals. The research was published today in Nature.
"It's been proposed that nanoparticles could really enhance the strength of metals without damaging their plasticity, especially light metals like magnesium, but no groups have been able to disperse ceramic nanoparticles in molten metals until now," said Xiaochun Li, the principal investigator on the research and Raytheon Chair in Manufacturing Engineering at UCLA. "With an infusion of physics and materials processing, our method paves a new way to enhance the performance of many different kinds of metals by evenly infusing dense nanoparticles to enhance the performance of metals to meet energy and sustainability challenges in today's society."
UCLA
Xiaochun Li
Structural metals are load-bearing metals; they are used in buildings and vehicles. Magnesium, at just two-thirds the density of aluminum, is the lightest structural metal. Silicon carbide is an ultra-hard ceramic commonly used in industrial cutting blades. The researchers' technique of infusing a large number of silicon carbide particles smaller than 100 nanometers into magnesium added significant strength, stiffness, plasticity and durability under high temperatures.
The researchers' new silicon carbide-infused magnesium demonstrated record levels of specific strength -- how much weight a material can withstand before breaking -- and specific modulus -- the material's stiffness-to-weight ratio. It also showed superior stability at high temperatures.
Ceramic particles have long been considered as a potential way to make metals stronger. However, with microscale ceramic particles, the infusion process results in a loss of plasticity.
Nanoscale particles, by contrast, can enhance strength while maintaining or even improving metals' plasticity. But nanoscale ceramic particles tend to clump together rather than dispersing evenly, due to the tendency of small particles to attract one other.
To counteract this issue, researchers dispersed the particles into a molten magnesium zinc alloy. The newly discovered nanoparticle dispersion relies on the kinetic energy in the particles' movement. This stabilizes the particles' dispersion and prevents clumping.
To further enhance the new metal's strength, the researchers used a technique called high-pressure torsion to compress it.
"The results we obtained so far are just scratching the surface of the hidden treasure for a new class of metals with revolutionary properties and functionalities," Li said.
The new metal (more accurately called a metal nanocomposite) is about 14 percent silicon carbide nanoparticles and 86 percent magnesium. The researchers noted that magnesium is an abundant resource and that scaling up its use would not cause environmental damage.
###
The paper's lead author is Lian-Yi Chen, who conducted the research as a postdoctoral scholar in Li's Scifacturing Laboratory at UCLA. Chen is now an assistant professor of mechanical and aerospace engineering at Missouri University of Science and Technology.
The paper's other authors from UCLA include Jia-Quan Xu, a graduate student in materials science and engineering; Marta Pozuelo, an assistant development engineer; and Jenn-Ming Yang, professor of materials science and engineering.
The other authors on the paper are Hongseok Choi, of Clemson University; Xiaolong Ma, of North Carolina State University; Sanjit Bhowmick of Hysitron, Inc. of Minneapolis; and Suveen Mathaudhu of UC Riverside.
The research was funded in part by the National Institute of Standards and Technology.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Matthew Chin
310-206-0680
Copyright © UCLA
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Automotive/Transportation
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Aerospace/Space
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








