Home > Press > Scientists blueprint tiny cellular 'nanomachine'
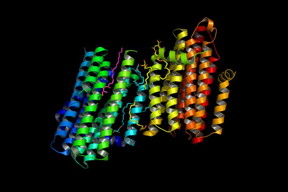 |
| Graphic shows the structure of diacylglycerol kinase (DgkA) determined with the Free Electron Laser (FEL) in Stanford, Ca. This new structure has been deposited in the protein data bank under the code 4UYO. CREDIT: The Biodesign Institute at Arizona State University |
Abstract:
Scientists have drawn up molecular blueprints of a tiny cellular 'nanomachine', whose evolution is an extraordinary feat of nature, by using one of the brightest X-ray sources on Earth.
Scientists blueprint tiny cellular 'nanomachine'
Tempe, AZ | Posted on December 17th, 2015The scientists produced the structural map of this nanomachine - diacylglycerol kinase - by using a "hit and run" crystallography technique. In doing so, they have been able to understand how the tiny enzyme performs critical cellular duties - answering questions that have been on the table for over 50 years about this 'paradigmatic protein'.
Kinases are key players in metabolism, cell signalling, protein regulation, cellular transport, secretory processes, and many other cellular pathways that allow us to function healthily. They coordinate the transfer of energy from certain molecules to specific substrates, affecting their activity, reactivity, and ability to bind other molecules.
Diacylglycerol kinase, the focus of this study, plays a role in bacterial cell wall synthesis. It is a small, integral membrane enzyme that coordinates a particularly complex reaction: its lipid substrate is hydrophobic (repelled by water) and resides in cell membranes, while its co-substrate, ATP, is entirely water soluble.
How it does this had remained a mystery for decades, but the newly produced blueprints have answered these questions.
"How this diminutive nanomachine, less than 10 nm tall, brings these two disparate substrates together at the membrane interface for reaction is revealed in a molecularly detailed crystal structure. It is the smallest known kinase, and seeing its form with crystal clarity is now helping us to answer questions that formed from over 50 years of work on this paradigmatic protein," said Professor of Membrane Structural and Functional Biology at Trinity College Dublin, Martin Caffrey.
Figuring out how this tiny machine works at the molecular level was enormously facilitated by our use of one of the brightest X-ray sources on Earth, the X-ray free-electron laser at the Stanford Linear Accelerator Center.
Professor Caffrey added: "This instrument produces bursts of X-rays just femtoseconds (a quad-trillionth of a second) long. With these short bursts we were able to obtain structural information about the enzyme before it vaporized through radiation damage in what I tritely refer to as 'Hit and Run' serial crystallography."
According to Petra Fromme, the director of the Center for Applied Structural Discovery at Arizona State University's Biodesign Institute and a co-author of the current study, "this is the first structure of a protein that is a membrane-integral enzyme and important biocatalyst in the cell." (Biocatalysts speed up the rate of critical biological reactions.)
The tiny kinase is one of the research targets for the NIH funded Center for Membrane Proteins in Infectious Diseases at ASU, which is devoted to unraveling the molecular basis of viral and bacterial proteins involved in diseases as well as the human proteins defending the body from pathogen attack.
The ASU team contributed to the work with expertise in crystal growth and sample injection, as well as data collection and evaluation.
In the future, the scientists hope to extend their free-electron laser work to make 'X-ray movies' of this remarkable nanomachine, so as to watch how it 'does chemistry' in atomic detail in real time.
The article describing the work has just been published in the leading journal Nature Communications.
###
The team of researchers at ASU includes the faculty Wei Liu, Petra Fromme and Raimund Fromme from the School of Molecular Sciences, and John Spence, Uwe Weierstall and Nadia Zatsepin from the Department of Physics, the researcher Ingo Grotjohann as well as the graduate students Shibom Basu, Christopher Kupitz and Kimberley Rendek.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
RICHARD HARTH
504-427-2666
Petra Fromme
Professor and Director
Center for Applied Structural Discovery
Biodesign Institute
Arizona State University
Petra Fromme
tel: 480)965-9028
Lab Phone: (480)965-8040
Martin Caffrey
Professor of Membrane Structural and Functional Biology
School of Biochemistry and Immunology
Trinity College Dublin
Tel: +353-1-896-4253 / +353-86-818-7704
Thomas Deane
Press Officer for the Faculty of Engineering
Mathematics and Science
Trinity College Dublin
Tel: +353-1-896-4685
Copyright © Arizona State University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
Videos/Movies
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Molecular Machines
![]() First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
![]() Nanotech scientists create world's smallest origami bird March 17th, 2021
Nanotech scientists create world's smallest origami bird March 17th, 2021
![]() Giant nanomachine aids the immune system: Theoretical chemistry August 28th, 2020
Giant nanomachine aids the immune system: Theoretical chemistry August 28th, 2020
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








