Home > Press > How nanoparticles give electrons away: FAU researchers gain new insights into the electrical charge of platinum particles
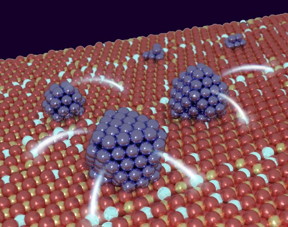 |
| Researchers have investigated how much electrical charge nanoparticles transfer to their support for the first time. CREDIT: Sergey Kozlov and Oriol Lamiel |
Abstract:
Whether it is in catalytic processes in the chemical industry, environmental catalysis, new types of solar cells or new electronic components, nanoparticles are everywhere in modern production and environmental technologies, where their unique properties ensure efficiency and save resources. The special properties of nanoparticles often arise from a chemical interaction with the support material that they are placed on. Such interactions often change the electronic structure of the nanoparticle because electrical charge is exchanged between the particle and the support. Working groups led by Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg (FAU) and the University of Barcelona have now succeeded in counting the number of elementary charges that are lost by a platinum nanoparticle when it is placed onto a typical oxide support. Their work brings the possibility of developing tailor-made nanoparticles a step closer.*
How nanoparticles give electrons away: FAU researchers gain new insights into the electrical charge of platinum particles
Nürnberg, Germany | Posted on December 15th, 2015One of the main questions that nanoscience researchers have been discussing for some time now is how nanoparticles interact with the support that they are placed on. It is now clear that various physical and chemical factors such as the electronic structure, the nanostructure and - crucially - their interaction with the support control the properties of nanoparticles. Although this interaction - specifically the transfer of electrical charge - has already been observed to a great extent, previous studies have not investigated how much charge is transferred and whether there is a relationship between the transfer and the size of the nanoparticle.
In order to measure the electrical charge that is exchanged the international team of researchers from Germany, Spain, Italy and the Czech Republic led by Prof. Dr. Jörg Libuda, Professor of Physical Chemistry, and Prof. Dr. Konstantin Neyman, University of Barcelona, prepared an extremely clean and atomically well-defined oxide surface, onto which they placed platinum nanoparticles. Using a highly sensitive detection method at Elettra Sincrotrone Trieste the researchers were able to quantify the effect for the first time. Looking at particles with various numbers of atoms, from several to many hundred, they counted the number of electrons transferred and showed that the effect is most pronounced for small nanoparticles with around 50 atoms. The magnitude of the effect is surprisingly large: approximately every tenth metal atom loses an electron when the particle is in contact with the oxide. The researchers were also able to use theoretical methods to show how the effect can be controlled, allowing the chemical properties to be adapted to better suit their intended application. This would allow valuable raw materials and energy to be used more efficiently in catalytic processes in the chemical industry, for example.
###
The project was funded in part by the EU and by FAU's Cluster of Excellence 'Engineering of Advanced Materials' (EAM). The researchers at EAM aim to bring together basic research in the natural sciences and applied research in engineering to investigate and develop new hierarchically structured materials with specific electronic, optical, catalytic and mechanical properties.
*doi: 10.1038/nmat4500
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Dr. Jörg Libuda
49-913-185-27308
Copyright © Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg (FAU)
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
Chemistry
![]() Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








