Home > Press > Clay makes better high-temp batteries: Rice University scientists develop materials to power devices in harsh environments
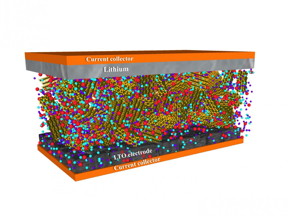 |
| Batteries with clay-based electrolyte/separators were tested at up to 120 degrees Celsius and showed strong performance over 120 charge-discharge cycles, according to scientists at Rice University. CREDIT: Kaushik Kalaga/Rice University |
Abstract:
A unique combination of materials developed at Rice University, including a clay-based electrolyte, may solve a problem for rechargeable lithium-ion batteries destined for harsh environments.
Clay makes better high-temp batteries: Rice University scientists develop materials to power devices in harsh environments
Houston, TX | Posted on November 11th, 2015The lithium-ion chemistry-based battery revealed this week is robust enough to supply stable electrochemical power in temperatures up to 120 degrees Celsius (248 degrees Fahrenheit). Such batteries could find use in space, defense and oil and gas applications, among others.
Chemist Pulickel Ajayan and his colleagues at Rice and at Wayne State University in Detroit describe the material this month in the American Chemical Society journal ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces.
This discovery, like earlier work on supercapacitors by the lab, depends on the malleable qualities of bentonite clay and room-temperature ionic liquids that serve as both a separator and an electrolyte system and provide a conductive path between a battery's anode and cathode.
"Clay naturally has a lot of moisture in it, and that's not a problem when you're doing supercapacitors," said Kaushik Kalaga, a graduate student in Ajayan's lab and lead author of the new study. "But a battery has to have a lithium-ion conductive species in the electrolyte to conduct lithium ions from the cathode or anode, or vice versa, when you charge and discharge.
"Lithium is very reactive with water, so our first challenge was to eliminate water from the clay while keeping its structure intact," he said.
Kalaga and his team started by baking commercial clay particles at 650 C for an hour to dry them out. They then combined a room-temperature ionic liquid and lithium salt and mixed them into the clay in an oxygen-free glove box. The liquefied salt acts as a source of lithium ions that conduct through the electrolyte to the electrodes.
The researchers spread the resulting peanut butter-like slurry between lithium metal electrodes and encapsulated them in coin-shaped batteries for testing at various temperatures.
Conventional organic electrolytes cannot be used in batteries over 60 C, due to their low boiling temperature; the vapors that form beyond 80 C can lead to an explosion, Kalaga said. Batteries that have solid-state electrolytes work in high temperatures, but the electrolytes don't connect as well with electrodes, which hurts performance.
The researchers built their composite electrolyte to be tough and conductive and still present the maximum surface area to electrodes to provide a solid path for current.
The units proved able to deliver current at high temperatures with a stable voltage window of 3 volts over 120 charge-discharge cycles and featured both the thermal stability of solid-state electrolytes and the wetting properties of liquid electrolytes, assuring good contact with the electrodes. The voltage window is the range between which the electrolyte is stable and is not chemically degraded.
"It's able to produce pretty good performance at room temperature, but it gets better at higher temperatures," Kalaga said. "The clay-based electrolyte gets less viscous but still retains its consistency at least to 150 C. The next step is to push the limits further."
The nature of the material makes it suitable for forming into many types of batteries, from thin films to commercial-scale units, the researchers wrote.
"There are many applications that need energy storage devices to work in extreme environments, and there needs to be innovation in the materials systems, particularly electrolytes, to expand the window of operation conditions," Ajayan said. "Our lab is at the forefront of discoveries in this area."
###
Co-authors of the paper are graduate student Marco-Tulio Rodrigues and postdoctoral research associate Hemtej Gullapalli of Rice and postdoctoral fellow Ganguli Babu and Rice alumnus Leela Mohana Reddy Arava, an assistant professor of mechanical engineering, both at Wayne State. Ajayan is chair of Rice's Department of Materials Science and NanoEngineering, the Benjamin M. and Mary Greenwood Anderson Professor in Engineering and a professor of chemistry.
The Advanced Energy Consortium supported the research.
####
About Rice University
Located on a 300-acre forested campus in Houston, Rice University is consistently ranked among the nation's top 20 universities by U.S. News & World Report. Rice has highly respected schools of Architecture, Business, Continuing Studies, Engineering, Humanities, Music, Natural Sciences and Social Sciences and is home to the Baker Institute for Public Policy. With 3,888 undergraduates and 2,610 graduate students, Rice's undergraduate student-to-faculty ratio is 6-to-1. Its residential college system builds close-knit communities and lifelong friendships, just one reason why Rice is ranked No. 1 for best quality of life and for lots of race/class interaction by the Princeton Review. Rice is also rated as a best value among private universities by Kiplinger's Personal Finance.
Follow Rice News and Media Relations via Twitter @RiceUNews
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
David Ruth
713-348-6327
Located on a 300-acre forested campus in Houston, Rice University is consistently ranked among the nation's top 20 universities by U.S. News & World Report. Rice has highly respected schools of Architecture, Business, Continuing Studies, Engineering, Humanities, Music, Natural Sciences and Social Sciences and is home to the Baker Institute for Public Policy. With 3,888 undergraduates and 2,610 graduate students, Rice's undergraduate student-to-faculty ratio is 6-to-1. Its residential college system builds close-knit communities and lifelong friendships, just one reason why Rice is ranked No. 1 for best quality of life and for lots of race/class interaction by the Princeton Review. Rice is also rated as a best value among private universities by Kiplinger's Personal Finance.
Copyright © Rice University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








