Home > Press > Nanobodies from camels enable the study of organ growth
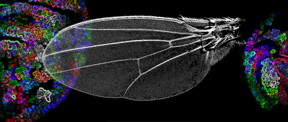 |
| Drosophila wing size control depends on the spreading of the Dpp morphogen. CREDIT: University of Basel, Biozentrum |
Abstract:
Researchers at the Biozentrum of the University of Basel have developed a new technique using nanobodies. Employing the so-called "Morphotrap", the distribution of the morphogen Dpp, which plays an important role in wing development, could be selectively manipulated and analyzed for the first time in the fruit fly. In the future, this tool may be applied for many further investigations of organ growth. The results of the study have been published in the current issue of Nature.
Nanobodies from camels enable the study of organ growth
Basel, Switzerland | Posted on November 9th, 2015The two basic processes that control organ development are the regulation of growth and of the spatial pattern. The research group of Prof. Markus Affolter at the Biozentrum, University of Basel, has now developed a method named "Morphotrap" to study wing development in the fruit fly.
Their results demonstrate that the signaling molecule Dpp, a so-called morphogen, influences growth in the center of the wing imaginal disc but not in the peripheral regions. It is the first time that an anti-GFP nanobody has been successfully employed in such an investigation. This tool also holds promise for future studies on organ development.
The new method "Morphotrap": Nanobodies to study growth
Nanobodies are small antibody fragments derived from camels. They enable the research team of Markus Affolter to manipulate molecules in the living organism. The so-called "Morphotrap" method employs anti-GFP nanobodies. Using these Nanobodies, the functions of GFP-tagged proteins in living organisms can be studied faster and more effectively than by conventional methods.
"These anti-GFP nanobodies inhibit the dispersal of the morphogen Dpp at different locations in the wing. Therefore they allow us to identify the influence of Dpp spreading on wing growth," explains Stefan Harmansa, the first author of the study.
Morphogen Dpp regulates growth in the middle of the imaginal disc
To determine the influence of the morphogen Decapentaplegic (Dpp) in more detail, the Affolter group examined the wing disc of the fruit fly, called the imaginal disc. This is the precursor tissue of the wing of the adult fly and serves as a model for studies on organ development.
"Our findings demonstrate that the morphogen Dpp only affects growth in the center of the imaginal disc. Growth continues in the periphery even when we fully block Dpp dispersal into this regions," explains Harmansa. "Now, by employing anti GFP nanobodies, we have been able to show to which extent the morphogen Dpp determines the wing size and consequently we could disprove one of the two predominant theories in this field," says Harmansa.
The fact that anti GFP-nanobodies can successfully be applied for research in complex living organism is a great achievement. Affolter also plans to apply this technique in future research: "In a next step, we will investigate at what time in development Dpp acts to control central growth. The correlation between the spatial and temporal influence of Dpp will provide new insights into organ growth and may uncover possible causes of organ malformation," says Affolter.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Yannik Sprecher
41-612-672-424
Copyright © University of Basel
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








