Home > Press > Capacitor breakthrough: Nanotechnology offers new approach to increasing storage ability of dielectric capacitors
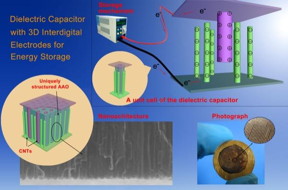 |
| This is a diagram of the dielectric capacitor research developed by a University of Delaware-led research team. CREDIT: Kathy F. Atkinson/University of Delaware |
Abstract:
Oct. 21, 2015, was the day that Doc Brown and Marty McFly landed in the future in their DeLorean, with time travel made possible by a "flux capacitor."
Capacitor breakthrough: Nanotechnology offers new approach to increasing storage ability of dielectric capacitors
Newark, DE | Posted on October 24th, 2015While the flux capacitor still conjures sci-fi images, capacitors are now key components of portable electronics, computing systems, and electric vehicles.
In contrast to batteries, which offer high storage capacity but slow delivery of energy, capacitors provide fast delivery but poor storage capacity.
A great deal of effort has been devoted to improving this feature -- known as energy density -- of dielectric capacitors, which comprise an insulating material sandwiched between two conducting metal plates.
Now, a group of researchers at the University of Delaware and the Chinese Academy of Sciences has successfully used nanotechnology to achieve this goal.
The work is reported in a paper, "Dielectric Capacitors with Three-Dimensional Nanoscale Interdigital Electrodes for Energy Storage," published in Science Advances, the first open-access, online-only journal of AAAS.
"With our approach, we achieved an energy density of about two watts per kilogram, which is significantly higher than that of other dielectric capacitor structures reported in the literature," says Bingqing Wei, professor of mechanical engineering at UD.
"To our knowledge, this is the first time that 3D nanoscale interdigital electrodes have been realized in practice," he adds. "With their high surface area relative to their size, carbon nanotubes embedded in uniquely designed and structured 3D architectures have enabled us to address the low ability of dielectric capacitors to store energy."
One of the keys to the success of the new capacitor is an interdigitated design -- similar to interwoven fingers between two hands with "gloves" -- that dramatically decreases the distance between opposing electrodes and therefore increases the ability of the capacitor to store an electrical charge.
Another significant feature of the capacitors is that the unique new three-dimensional nanoscale electrode also offers high voltage breakdown, which means that the integrated dielectric material (alumina, Al2O3) does not easily fail in its intended function as an insulator.
"In contrast to previous versions, we expect our newly structured dielectric capacitors to be more suitable for field applications that require high energy density storage, such as accessory power supply and hybrid power systems," Wei says.
###
About the research
Co-authors on the paper include Fangming Han, Guowen Meng, Fei Zhou, Li Song, Xinhua Li, Xiaoye Hu, Xiaoguang Zhu, Bing Wu and Bingqing Wei.
The work was funded by the National Key Basic Research Program of China, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the CAS/SAFEA (Chinese Academy of Sciences/State AQ9 Administration of Foreign Experts Affairs) International Partnership Program for Creative Research Teams, and the Anhui Provincial Natural Science Foundation.
Wei was involved in experimental design and data analysis. The samples were prepared and characterized by his colleagues in China.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Peter Bothum
302-831-1421
Copyright © University of Delaware
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Automotive/Transportation
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








