Home > Press > Scientists demonstrate how to improve ultrathin CIGSe solar cells by nanoparticles
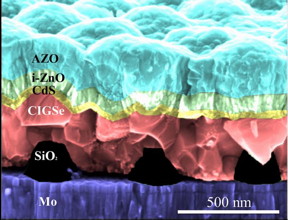 |
| The SiO2 nanoparticles (black) have been imprinted directly on the molybdenum substrate (purple) which corresponds to the back contact of the solar cell. On top of this structured substrate the ultrathin CIGSe layer (red) was grown at HZB, and subsequently all the other layers and contacts needed for the solar cell. Since all layers are extremely thin, even the top layer is showing deformations according to the pattern of the nanoparticles. CREDIT: G.Yin / HZB |
Abstract:
Nanoparticles with sizes the order of a wavelength interact with light in specific ways. A young investigator group at Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin, led by Professor Martina Schmid, is inquiring how to use arrangements of such nanoparticles to improve solar cells and other opto-electronic devices. Now the scientists report in the Journal of the American Chemical Society ACS Nano a considerable success with ultrathin CIGSe solar cells.
Scientists demonstrate how to improve ultrathin CIGSe solar cells by nanoparticles
Berlin, Germany | Posted on October 19th, 2015Problems add up below 1 micrometer
CIGSe solar cells have proven high efficiencies and are established thin film devices with active layers of a few micrometers thickness. But since Indium is a rare element, the active layer should be as thin as possible. This reduces the efficiency, since less light is absorbed. And if the active layer is thinner than one micrometer, an additional problem arises: more and more charge carriers meet and recombine at the back contact, getting "lost".
Ultrathin CIGSe cell with efficiencies of 11.1%
"It took me more than one year to be able to produce ultrathin layers of only 0.46 micrometer or 460 nanometers which still reach reasonable efficiencies up to 11.1 %," Guanchao Yin says about his PhD project. He then started to enquire how to implement nanoparticles between different layers of the solar cell. His supervisor Martina Schmid discussed this with Prof. Albert Polman, one of the pioneers in the field of nanophotonics, at the Center for Nanooptics, Amsterdam, with whom she was in contact for a while already. They proposed to produce arrays of dielectric nanoparticles by nanoimprinting technologies.
No big effect by nanoparticles on top
In a first step, the colleagues in Amsterdam implemented a pattern of dielectric TiO2-nanoparticles on top of Yin's ultrathin solar cells; the idea was that they would act as light traps and increase absorption in the CIGSe layer. But this did not increase the efficiency as much as proved in Si-based solar cells. Yin then continued testing and ultimately found out what worked best: a nanoparticle array not on top but at the back contact of the cell!
Nanoparticles at the back contact: effiency increases to 12.3%
The colleagues from Amsterdam produced an array of SiO2 nanoparticles, directly on the Molybdenum substrate which corresponds to the back contact of the solar cell. On top of this structured substrate the ultrathin CIGSe layer was grown by Yin, and subsequently all the other layers and contacts needed for the solar cell. With this configuration, the efficiency increased from 11.1 % to 12.3 %, and the short circuit current density of the ultrathin CIGSe cells increased by more than 2 mA/cm2. With additional anti-reflective nanoparticles at the front efficiencies raised even to 13.1%.
Light trapping and prevention of charge carrier loss
"This leads to efficient light trapping and does not deteriorate the cell," Yin explains. Further studies indicate that the nanoarray of dielectric SiO2 nanoparticles at the back side could also increase efficiency by reducing chances for charge carrier recombination. "This work is just a start, we have now new ideas for further designs to enhance absorption and reduce recombination, thus increasing efficiencies by making use of optical and electrical benefits of the nanoparticles," Martina Schmid says.
###
to the paper:
M.-C. van Lare*, G. Yin*, A. Polman, M. Schmid "Light coupling and trapping in ultra-thin Cu(In,Ga)Se2 solar cells using dielectric scattering patterns" ACS Nano DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.5b04091 (2015), *equal contribution
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Dr. Martina Schmid
49-308-062-43243
Copyright © Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin für Materialien und Energie
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
![]() Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








