Home > Press > Silver: The promising electrode winner for low-cost perovskite solar cells
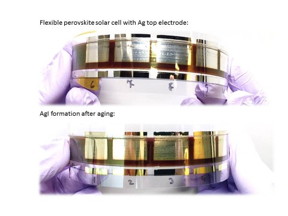 |
| Flexible perovskite solar cell device before (top) and after (bottom) corrosion of the silver electrode (Energy Materials and Surface Sciences Unit, OIST). The device prepared by Dr. Mikas Remeika. |
Abstract:
Perovskite solar cells are the rising star in photovoltaics. They absorb light across almost all visible wavelengths, they have exceptional power conversion efficiencies exceeding 20% in the lab, and they are relatively easy to fabricate. So, why are perovskite solar cells yet to be found on the top of our roofs? One problem is their overall cost, and another is that cheaper perovskite solar cells have a short lifespan. A study published in Advanced Materials Interfaces by the Energy Materials and Surface Sciences Unit at the Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology Graduate University (OIST), reveals a cause for the short lifetime of perovskite solar cells with silver electrodes.
Proposed mechanism of the silver corrosion
The animation shows the layers of the perovskite solar cell and the proposed mechanism of corrosion of the silver electrode. Water molecules diffuse through the pinholes of the spiro-MeOTAD layer and induce the decomposition of the perovskite producing iodine-containing compounds. The iodine-containing compounds migrate to the silver layer, and corrode it. This can explain why silver iodide is found on corroded solar cells. (Energy Materials and Surface Sciences Unit, OIST)
Silver: The promising electrode winner for low-cost perovskite solar cells
Okinawa, Japan | Posted on October 15th, 2015Currently, the most common electrode material in perovskite solar cells is gold, which is extremely expensive. A low-cost alternative to gold is silver, around 65 times cheaper. To keep the cost even lower, the team wants to use solution-processed method to fabricate the layers of the solar cell, instead of expensive vacuum-based techniques. The problem of using silver electrodes and the solution-based method is that silver gets corroded within days of the solar cell fabrication. The corrosion makes the electrode turn yellow, and reduces the efficiency of the cell. The OIST team, headed by Prof. Yabing Qi, has demonstrated the cause of this degradation and proposed an explanation.
Perovskite solar cells are composed of a sandwich of layers that work together to transform light into electricity. Light is absorbed by the perovskite material and stimulates electron excitations, generating the so-called electron-hole pairs. In simple terms: when electrons are excited, they “jump and leave holes behind.” Excited electrons and holes are transported in opposite directions by the adjacent layers of the solar cells, comprising of an electron-transport titanium dioxide layer, a spiro-MeOTAD hole-transport layer (HTL), a glass layer coated with a transparent conductive material, and a silver top electrode. The whole mechanism generates current, but it needs the correct functioning of each layer of the solar cell in order to work efficiently. “If one layer fails, the whole solar cell will suffer,” explains Luis Ono, a staff scientist and group leader in Prof. Qi’s unit. In this study, the team analysed the composition of the corroded silver electrode and identified the formation of silver iodide as the reason for the electrode corrosion. The color change was due to the oxidation from silver to silver iodide. They also found that exposure to air accelerates the corrosion, when compared to dry nitrogen gas exposure. The team proposed a mechanism for this damage: silver iodide forms because gas molecules from ambient air reach the perovskite material and degrade it forming iodine containing compounds. These iodine-containing compounds diffuse to the silver electrode and corrode it. The migration of both air molecules and iodine-containing compounds could happen through small pinholes present in the spiro-MeOTAD HTL layer (see animation). The pinholes present in the spiro-MeOTAD HTL layer produced with the solution-processed method were identified some months ago by Zafer Hawash, a PhD student in the same laboratory.
Replacing gold with silver and using the solution-processed method are key to bringing down the cost of the solar cells. The OIST team believes that understanding the corrosion mechanism is the first step in increasing the electrode lifetime. Since preventing the formation of pinholes in the spiro-MeOTAD HTL layer is essential for a longer cell lifetime, the team is also working on producing pinhole-free solar cells with the solution-process method, while the production of pinhole-free HTL with the vacuum-based method has already been published by the same group. “Perovskite-based solar cells show potential for commercial use as the next generation photovoltaic technology. Our goal is to design and fabricate large-area and low-cost photovoltaic modules with extended lifetime by employing appropriate HTLs and encapsulation materials,” explains Qi.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Natori Kaoru
Copyright © Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology Graduate Univers
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Videos/Movies
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() New X-ray imaging technique to study the transient phases of quantum materials December 29th, 2022
New X-ray imaging technique to study the transient phases of quantum materials December 29th, 2022
![]() Solvent study solves solar cell durability puzzle: Rice-led project could make perovskite cells ready for prime time September 23rd, 2022
Solvent study solves solar cell durability puzzle: Rice-led project could make perovskite cells ready for prime time September 23rd, 2022
![]() Scientists prepare for the world’s smallest race: Nanocar Race II March 18th, 2022
Scientists prepare for the world’s smallest race: Nanocar Race II March 18th, 2022
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
![]() Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








