Home > Press > Organic semiconductors get weird at the edge: University of British Columbia research
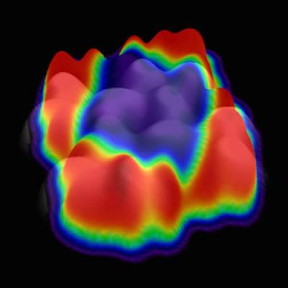 |
| This composite image shows the difference in electronic states at the edge of the material compared to molecules in the centre. CREDIT: University of British Columbia |
Abstract:
As the push for tinier and faster electronics continues, a new finding by University of British Columbia scientists could help inform the design of the next generation of cheaper, more efficient devices.
Organic semiconductors get weird at the edge: University of British Columbia research
Vancouver, Canada | Posted on October 7th, 2015The work, published this week in Nature Communications, details how electronic properties at the edges of organic molecular systems differ from the rest of the material.
Organic materials--plastics--are of great interest for use in solar panels, light emitting diodes and transistors. They're low-cost, light, and take less energy to produce than silicon. Interfaces--where one type of material meets another--play a key role in the functionality of all these devices.
"We found that the polarization-induced energy level shifts from the edge of these materials to the interior are significant, and can't be neglected when designing components," says UBC PhD researcher Katherine Cochrane, lead author of the paper.
'While we were expecting some differences, we were surprised by the size of the effect and that it occurred on the scale of a single molecule," adds UBC researcher Sarah Burke, an expert on nanoscale electronic and optoelectronic materials and author on the paper.
The researchers looked at 'nano-islands' of clustered organic molecules. The molecules were deposited on a silver crystal coated with an ultra-thin layer of salt only two atoms deep. The salt is an insulator and prevents electrons in the organic molecules from interacting with those in the silver--the researchers wanted to isolate the interactions of the molecules.
Not only did the molecules at the edge of the nano-islands have very different properties than in the middle, the variation in properties depended on the position and orientation of other molecules nearby.
The researchers, part of UBC's Quantum Matter Institute, used a simple, analytical model to explain the differences which can be extended to predict interface properties in much more complex systems, like those encountered in a real device.
"Herbert Kroemer said in his Nobel Lecture that 'The interface is the device' and it's equally true for organic materials," says Burke. "The differences we've seen at the edges of molecular clusters highlights one effect that we'll need to consider as we design new materials for these devices, but likely they are many more surprises waiting to be discovered."
Cochrane and colleagues plan to keep looking at what happens at interfaces in these materials and to work with materials chemists to guide the design rules for the structure and electronic properties of future devices.
Methods
The experiment was performed at UBC's state-of-the-art Laboratory for Atomic Imaging Research, which features three specially designed ultra-quiet rooms that allow the instruments to sit in complete silence, totally still, to perform their delicate measurements. This allowed the researchers to take dense data sets with a tool called a scanning tunnelling microscope (STM) that showed them the energy levels in real-space on the scale of single atoms.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Chris Balma
604-822-5082
Copyright © University of British Columbia
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
Chemistry
![]() Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Display technology/LEDs/SS Lighting/OLEDs
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








