Home > Press > Research improves efficiency from larger perovskite solar cells
 |
| A new fabrication method enabled researchers to make larger perovskite cells with few defects, helping to maintain efficiency at larger cell sizes. CREDIT: Brown University / NREL |
Abstract:
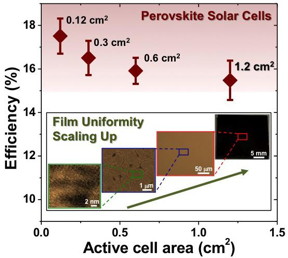
Using a newly developed fabrication method, a research team has attained better than a 15-percent energy conversion efficiency from perovskite solar cells larger than one square centimeter area. The researchers, from Brown University and the National Renewable Energy Lab (NREL), have reported their findings in the journal Advanced Materials.
Research improves efficiency from larger perovskite solar cells
Providence, RI | Posted on October 6th, 2015Perovskites, materials with a particular crystalline structure, have caused quite a buzz in the solar energy world. Perovskite solar cells are relatively cheap to make, and the efficiency with which they can convert sunlight into electricity has been increasing rapidly in recent years. Researchers have reported efficiency in perovskite cells of higher than 20 percent, which rivals traditional silicon cells. Those high efficiency ratings, however, have been achieved using cells only a tenth of a square centimeter -- fine for lab testing, but too small to be used in a solar panel.
"The use of tiny cells for efficiency testing has prompted some to question comparison of perovskite solar cells with other established photovoltaic technologies," said Nitin Padture, professor of engineering at Brown, director of Brown's Institute for Molecular and Nanoscale Innovation, and one of the senior authors of the new research. "But here we have shown that it is feasible to obtain 15-percent efficiency on cells larger than a square centimeter through improved processing. This is real progress."
Maintaining high efficiency on larger perovskite cells has proved to be a challenge, Padture says. "The problem with perovskite has been that when you try to make larger films using traditional methods, you get defects in the film that decrease efficiency."
The fabrication process that the Brown and NREL researchers reported in this latest paper builds on a previously reported method developed by Yuanyuan Zhou, a graduate student in Padture's lab. Perovskite precursors are dissolved in a solvent and coated onto a substrate. Then the substrate is bathed in a second solvent (called anti-solvent) that selectively grabs the precursor-solvent and whisks it away. What's left is an ultra-smooth film of perovskite crystals.
In this new study Zhou and Mengjin Yang, a postdoctoral researcher at NREL, developed a trick to grow the perovskite crystals to a larger size. The trick is to add excess organic precursor that initially "glues" the small perovskite crystals and helps them merge into larger ones during a heat-treatment, which then bakes away the excess precursor.
"The full coverage and uniformity over a large area come from the solvent method," Padture said. "Once we have that coverage, then we increase the size of the crystals. That gives us a film with fewer defects and higher efficiency." The 15-percent efficiency reached in this latest work is a good start, Padture said, but there's still room to improve. Ultimately, he would like to reach 20 to 25 percent in large-area cells, and he thinks that mark could be within reach using this method or a similar one.
Padture and colleagues at the University of Nebraska-Lincoln were recently awarded a $4-million grant by the National Science Foundation to expand their perovskite research.
###
Other authors on the paper were Yining Zeng, Chun-Sheng Jiang, and Kai Zhu of NREL. The work was supported by the U.S. Department of Energy (DE-AC36-08-GO28308 and DE-FOA-0000990) and the National Science Foundation (DMR-1305913).
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Kevin Stacey
401-863-3766
Copyright © Brown University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
![]() Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








