Home > Press > Graphene teams up with two-dimensional crystals for faster data communications
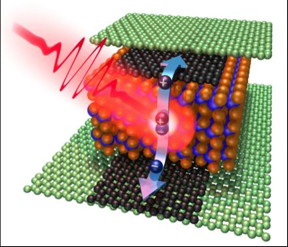 |
| Graphene/WSe2 (2-D material)/graphene heterostructure. CREDIT: ICFO-Fabien Vialla |
Abstract:
Ultra-fast detection of light lies at the heart of optical communication systems nowadays. Driven by the internet of things and 5G, data communication bandwidth is growing exponentially, thus requiring even faster optical detectors that can be integrated into photonic circuits.
Graphene teams up with two-dimensional crystals for faster data communications
Barcelona, Spain | Posted on October 5th, 2015In the recent work published today in Nature Nanotechnology, the research group led by Prof at ICFO Frank Koppens has shown that a two-dimensional crystal, combined with graphene, has the capability to detect optical pulses with a response faster than ten picoseconds, while maintaining a high efficiency. By using ultra-fast laser pulses, the researchers have shown a record-high photo-response speed for a heterostructure made of two-dimensional materials. These new materials are gaining more and more attention due to their amazing and rich variety of properties.
An important advantage of these devices based on graphene and other two-dimensional materials is that they can be integrated monolithically with silicon photonics enabling a new class of photonic integrated circuits. Although this study has been focused on the intrinsic properties of the photo-detection device, the next step is to develop prototype photonic circuitry and explore ways to improve large-scale production of these devices.
While Prof. Frank Koppens comments "It is remarkable how a material which is just a few nanometers thick can have such high performance", ICFO researcher Mathieu Massicotte and first author of this study states that "Everyone knew graphene could make ultrafast photodetectors, but related two-dimensional crystals were still lagging very much behind. In our work we show that by teaming up these two materials, we can obtain a photodetector that is not only ultrafast but also highly efficient."
The results obtained from this study have shown that the stacking of semiconducting 2D materials with graphene in heterostructures could lead to new, fast and efficient optoelectronic applications, such as high-speed integrated communication systems.
###
This study has been possible thanks to the support of the Fundació Cellex Barcelona, the European Research Council (ERC) and the EC under the Graphene Flagship, among others.
####
About ICFO-The Institute of Photonic Sciences
ICFO-The Institute of Photonic Sciences is a center of research excellence devoted to the science and technologies of light with a triple mission: to conduct frontier research, train the next generation of scientists, and provide knowledge and technology transfer.
Research at ICFO targets the forefront of science and technology based on light with programs directed at applications in Health, Renewable Energies, Information Technologies, Security and Industrial processes, among others. The institute hosts 300 professionals based in a dedicated building situated in the Mediterranean Technology Park in the metropolitan area of Barcelona.
ICFO participates in a large number of projects and international networks of excellence and is host to the NEST program financed by the Fundació Privada Cellex Barcelona. ICFO is a member of the Severo Ochoa Excelence program and a member of The Barcelona Institute of Science and Technology.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Alina Hirschmann
34-935-542-246
Copyright © ICFO-The Institute of Photonic Sciences
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Link to the research group led by Prof. at ICFO Frank Koppens:
Link to the research group led by Prof. at ICFO Frank Koppens:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Wireless/telecommunications/RF/Antennas/Microwaves
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Videos/Movies
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








