Home > Press > Brightness-equalized quantum dots improve biological imaging
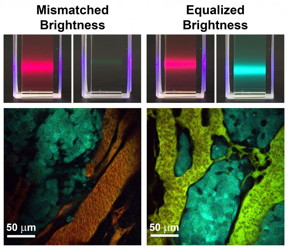 |
| Left: Conventional fluorescent materials like quantum dots and dyes have mismatched brightness between different colors. When these materials are administered to a tumor (shown below) to measure molecular concentrations, the signals are dominated by the brighter fluorophores. Right: New brightness-equalized quantum dots that have equal fluorescence brightness for different colors. When these are administered to tumors, the signals are evenly matched, allowing measurement of many molecules at the same time. CREDIT: University of Illinois |
Abstract:
Researchers at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign have introduced a new class of light-emitting quantum dots (QDs) with tunable and equalized fluorescence brightness across a broad range of colors. This results in more accurate measurements of molecules in diseased tissue and improved quantitative imaging capabilities.
Brightness-equalized quantum dots improve biological imaging
Urbana, IL | Posted on October 5th, 2015"In this work, we have made two major advances--the ability to precisely control the brightness of light-emitting particles called quantum dots, and the ability to make multiple colors equal in brightness," explained Andrew M. Smith, an assistant professor of bioengineering at Illinois. "Previously light emission had an unknown correspondence with molecule number. Now it can be precisely tuned and calibrated to accurately count specific molecules. This will be particularly useful for understanding complex processes in neurons and cancer cells to help us unravel disease mechanisms, and for characterizing cells from diseased tissue of patients."
"Fluorescent dyes have been used to label molecules in cells and tissues for nearly a century, and have molded our understanding of cellular structures and protein function. But it has always been challenging to extract quantitative information because the amount of light emitted from a single dye is unstable and often unpredictable. Also the brightness varies drastically between different colors, which complicates the use of multiple dye colors at the same time. These attributes obscure correlations between measured light intensity and concentrations of molecules," stated Sung Jun Lim, a postdoctoral fellow and first author of the paper, "Brightness-Equalized Quantum Dots," published this week in Nature Communications.
According to the researchers, these new materials will be especially important for imaging in complex tissues and living organisms where there is a major need for quantitative imaging tools, and can provide a consistent and tunable number of photons per tagged biomolecule. They are also expected to be used for precise color matching in light-emitting devices and displays, and for photon-on-demand encryption applications. The same principles should be applicable across a wide range of semiconducting materials.
"The capacity to independently tune the QD fluorescence brightness and color has never before been possible, and these BE-QDs now provide this capability," said Lim. "We have developed new materials-engineering principles that we anticipate will provide a diverse range of new optical capabilities, allow quantitative multicolor imaging in biological tissue, and improve color tuning in light-emitting devices. In addition, BE-QDs maintain their equal brightness over time while whereas conventional QDs with mismatched brightness become further mismatched over time. These attributes should lead to new LEDs and display devices not only with precisely matched colors--better color accuracy and brightness--but also with improved performance lifetime and improved ease of manufacturing." QDs are already in use in display devices (e.g. Amazon Kindle and a new Samsung TV).
###
In addition to Lim and Smith, co-authors include Mohammad U. Zahid, Phuong Le, Liang Ma, Bioengineering at Illinois; David Entenberg, Allison S. Harney, and John Condeelis, Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Andrew M. Smith
217-300-5638
Copyright © University of Illinois College of Engineering
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
Display technology/LEDs/SS Lighting/OLEDs
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Quantum Dots/Rods
![]() A new kind of magnetism November 17th, 2023
A new kind of magnetism November 17th, 2023
![]() IOP Publishing celebrates World Quantum Day with the announcement of a special quantum collection and the winners of two prestigious quantum awards April 14th, 2023
IOP Publishing celebrates World Quantum Day with the announcement of a special quantum collection and the winners of two prestigious quantum awards April 14th, 2023
![]() Qubits on strong stimulants: Researchers find ways to improve the storage time of quantum information in a spin rich material January 27th, 2023
Qubits on strong stimulants: Researchers find ways to improve the storage time of quantum information in a spin rich material January 27th, 2023
![]() NIST’s grid of quantum islands could reveal secrets for powerful technologies November 18th, 2022
NIST’s grid of quantum islands could reveal secrets for powerful technologies November 18th, 2022
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








