Home > Press > Semiconductor nanoparticles show high luminescence in a polymer matrix: Highly luminescent semiconductor nanoparticles immobilized in a polymer matrix using environmentally benign supercritical CO2
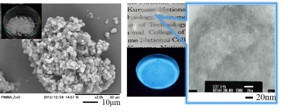 |
| Polymer-ZnO nanoparticle QDs by dispersion polymerization in supercritical CO2 are shown.
COPYRIGHT (C) 2015 TOYOHASHI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. |
Abstract:
Semiconductor nanocrystals known as quantum dots (QDs) are increasingly being used as photoluminescent materials in bio-imaging, photonics, and optoelectronic applications. However, these QDs must have stable photoluminescence properties to be used in these applications. Photoluminescence stability of QDs is achieved by chemically modifying the surface of the QDs.
Semiconductor nanoparticles show high luminescence in a polymer matrix: Highly luminescent semiconductor nanoparticles immobilized in a polymer matrix using environmentally benign supercritical CO2
Toyohashi, Japan | Posted on October 1st, 2015However, chemical modification of the surface typically requires large amounts of organic solvents that are harmful to the environment. To solve this problem, many researchers have attempted to synthesize polymer-nanoparticle composites by using supercritical fluid (SCF)-based technology. Supercritical CO2 has emerged as the most extensively studied SCF medium, because it is readily available, inexpensive, nonflammable, and environmentally benign.
Toyohashi Tech researchers in cooperation with researchers at the National Institute of Technology, Kurume College have investigated the formation of nanostructured material using supercritical CO2. They have demonstrated the formation of composite nanoparticles of luminescent ZnO QDs and polymer by dispersion polymerization in supercritical CO2. As a result of the supercritical-CO2-assisted surface modification of QDs, the QDs were well dispersed in the polymer matrix and showed high luminescence.
"Unfortunately, the photoluminescence properties of pristine luminescent QDs were quenched in supercritical CO2. The surface structure of the QDs was destroyed by supercritical CO2.", explains associate professor Kiyoshi Matsuyama at the National Institute of Technology, Kurume College, "We found that the quenching of ZnO QDs could be prevented by coating with silica to obtain PMMA-ZnO composite QDs with high luminescence using a supercritical-CO2-assisted surface modification with polymer."
Our research shows that the supercritical-fluid-assisted process provides an environmentally benign route for producing stabilized luminescent materials.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Michiteru Kitazaki
Copyright © Toyohashi University of Technology
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Related studies are featured in the September 2015 issue of TUT Research:
Related studies are featured in the September 2015 issue of TUT Research:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Quantum Dots/Rods
![]() A new kind of magnetism November 17th, 2023
A new kind of magnetism November 17th, 2023
![]() IOP Publishing celebrates World Quantum Day with the announcement of a special quantum collection and the winners of two prestigious quantum awards April 14th, 2023
IOP Publishing celebrates World Quantum Day with the announcement of a special quantum collection and the winners of two prestigious quantum awards April 14th, 2023
![]() Qubits on strong stimulants: Researchers find ways to improve the storage time of quantum information in a spin rich material January 27th, 2023
Qubits on strong stimulants: Researchers find ways to improve the storage time of quantum information in a spin rich material January 27th, 2023
![]() NISTís grid of quantum islands could reveal secrets for powerful technologies November 18th, 2022
NISTís grid of quantum islands could reveal secrets for powerful technologies November 18th, 2022
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








