Home > Press > A small, inexpensive high frequency comb signal generator: Researchers in Italy have calculated that the Nobel Prize-winning device called a Josephson junction could precisely convert a signal from megahertz to gigahertz -- with potential uses in metrology and telecommunications
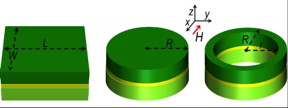 |
| Josephson junctions consist of a thin layer of insulator sandwiched between two superconducting layers. Researchers from Italy found that Josephson junctions placed in an oscillating magnetic field produced voltage pulses and that changing the shape of the Josephson junction changed the amount of power at different output frequencies. A ring-shaped junction produced more power at higher harmonics than did a circular or rectangular junction. CREDIT: P. Solinas, et al. / JAP |
Abstract:
The manipulation of electromagnetic radiation is an essential function of today's technology. Low frequency radiation -- in the kilohertz and megahertz range -- is easier to generate than gigahertz radiation. Yet higher frequencies can carry more information and travel farther.
A small, inexpensive high frequency comb signal generator: Researchers in Italy have calculated that the Nobel Prize-winning device called a Josephson junction could precisely convert a signal from megahertz to gigahertz -- with potential uses in metrology and telecommunications
Washington, DC | Posted on September 16th, 2015Now researchers from the Italian National Research Council (SPIN-CNR) and the National Enterprise for nanoScience and nanoTechnology (NEST-CNR) in Italy have devised a novel, inexpensive way to turn low frequency signals into higher frequencies. The approach makes use of a Nobel Prize-winning device called a Josephson junction, which is currently used to make extremely sensitive voltmeters and detect minute changes in magnetic fields. The researchers describe their new application in the Journal of Applied Physics, from AIP Publishing.
Josephson junctions consist of a thin layer of insulator sandwiched between two superconducting layers. Under the right conditions, electrons can travel from one superconducting layer to the other with no resistance through the insulator in the middle. When the current reaches a critical level, however, a finite resistance suddenly appears and a voltage develops across the device.
Paolo Solinas, a physicist at the Italian National Research Council, was experimenting on Josephson junctions with his colleagues at NEST-CNR when they noticed an unusual behavior. They found that Josephson junctions placed in an oscillating magnetic field produced voltage pulses. The researchers turned to theory to analyze and explain the behavior.
They found that an oscillating magnetic field produced a sudden jump in a quantum mechanical property of the superconductor layers called a phase. The phase jump in turn produced the voltage pulse. The researchers also found that a regularly time-dependent magnetic field would produce voltage pulses that contained hundreds of harmonics of the original driving frequency, including frequencies thousands of times higher.
"The output of a single device is small, but you could build an array of devices to turn low power intrinsic of a single junction into higher output power," Solinas said. The team calculated that stringing together 1,000 Josephson junctions made from niobium and aluminum oxide could convert a 100 MHz input frequency into a 100 picowatt signal at 50 GHz.
The researchers also found that changing the shape of the Josephson junction changed the amount of power at different output frequencies. They found that a ring-shaped junction produced more power at higher harmonics than did a circular or rectangular junction.
A frequency converter made from Josephson junctions would be a totally different type of signal generator from what's currently used, Solinas noted. Most gigahertz signal generators are bulky and expensive. Electronic circuits made from Josephson junctions could be mere millimeters long and integrate easily into electronic chips.
"So far we have theoretical results, but we are really looking forward to having a match with experiment," Solinas said. The team hopes their initial finding will interest others in building the devices. At first the technology would likely be used in the lab to calibrate measurements and perform experiments, Solinas said. With further development, it might also be used by the telecommunications industry.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
ason Socrates Bardi
240-535-4954
Copyright © American Institute of Physics
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Wireless/telecommunications/RF/Antennas/Microwaves
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








