Home > Press > Nanoporous gold sponge makes DNA detector: Possible new rapid tests for human, animal, plant pathogens
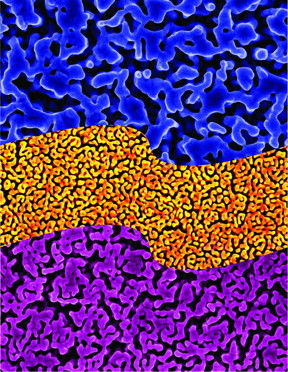 |
| Nanoporous gold contains tiny pores that can filter DNA from other biomolecules. The material can be used to make DNA detection devices for use in diagnostics. CREDIT: Erkin Seker, UC Davis |
Abstract:
Sponge-like nanoporous gold could be key to new devices to detect disease-causing agents in humans and plants, according to UC Davis researchers.
Nanoporous gold sponge makes DNA detector: Possible new rapid tests for human, animal, plant pathogens
Davis, CA | Posted on September 6th, 2015In two recent papers in Analytical Chemistry, a group from the UC Davis Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering demonstrated that they could detect nucleic acids using nanoporous gold, a novel sensor coating material, in mixtures of other biomolecules that would gum up most detectors. This method enables sensitive detection of DNA in complex biological samples, such as serum from whole blood.
"Nanoporous gold can be imagined as a porous metal sponge with pore sizes that are a thousand times smaller than the diameter of a human hair," said Erkin ?eker, assistant professor of electrical and computer engineering at UC Davis and the senior author on the papers. "What happens is the debris in biological samples, such as proteins, is too large to go through those pores, but the fiber-like nucleic acids that we want to detect can actually fit through them. It's almost like a natural sieve."
Rapid and sensitive detection of nucleic acids plays a crucial role in early identification of pathogenic microbes and disease biomarkers. Current sensor approaches usually require nucleic acid purification that relies on multiple steps and specialized laboratory equipment, which limit the sensors' use in the field. The researchers' method reduces the need for purification.
"So now we hope to have largely eliminated the need for extensive sample clean-up, which makes the process conducive to use in the field," ?eker said.
The result is a faster and more efficient process that can be applied in many settings.
The researchers hope the technology can be translated into the development of miniature point-of-care diagnostic platforms for agricultural and clinical applications.
"The applications of the sensor are quite broad ranging from detection of plant pathogens to disease biomarkers," said ?eker.
For example, in agriculture, scientists could detect whether a certain pathogen exists on a plant without seeing any symptoms. And in sepsis cases in humans, doctors might determine bacterial contamination much more quickly than at present, preventing any unnecessary treatments.
###
Other authors of the studies were Pallavi Daggumati, Zimple Matharu, and Ling Wang in the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering at UC Davis.
This work is funded by the UC Davis Research Investments in the Sciences and Engineering (RISE) program, which encourages interdisciplinary work to solve problems facing the world today, as well as the UC Lab Fees Research Program and the National Science Foundation.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Andy Fell
530-752-4533
Copyright © UC Davis
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Food/Agriculture/Supplements
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() SMART researchers pioneer first-of-its-kind nanosensor for real-time iron detection in plants February 28th, 2025
SMART researchers pioneer first-of-its-kind nanosensor for real-time iron detection in plants February 28th, 2025
![]() Silver nanoparticles: guaranteeing antimicrobial safe-tea November 17th, 2023
Silver nanoparticles: guaranteeing antimicrobial safe-tea November 17th, 2023
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








