Home > Press > Manchester team reveal new, stable 2-D materials: Dozens of new 2-dimensional materials similar to graphene are now available, thanks to research from University of Manchester scientists
 |
Abstract:
The problem has been that the vast majority of these atomically thin 2D crystals are unstable in air, so react and decompose before their properties can be determined and their potential applications investigated.
Manchester team reveal new, stable 2-D materials: Dozens of new 2-dimensional materials similar to graphene are now available, thanks to research from University of Manchester scientists
Manchester, UK | Posted on August 20th, 2015Writing in Nano Letters, the University of Manchester team demonstrate how tailored fabrication methods can make these previously inaccessible materials useful.
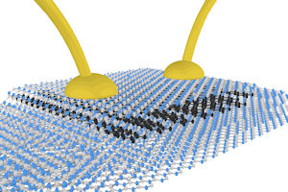
By protecting the new reactive crystals with more stable 2D materials, such as graphene, via computer control in a specially designed inert gas chamber environments, these materials can be successfully isolated to a single atomic layer for the first time.
Combining a range of 2D materials in thin stacks give scientists the opportunity to control the properties of the materials, which can allow 'materials-to-order' to meet the demands of industry.
High-frequency electronics for satellite communications, and light weight batteries for mobile energy storage are just two of the application areas that could benefit from this research. The breakthrough could allow for many more atomically thin materials to be studied separately as well as serve as building blocks for multilayer devices with such tailored properties.
The team, led by Dr Roman Gorbachev, used their unique fabrication method on two particular two-dimensional crystals that have generated intense scientific interest in the past 12 months but are unstable in air: black phosphorus and niobium diselenide.
The technique the team have pioneered allows the unique characteristics and excellent electronic properties of these air-sensitive 2D crystals to be revealed for the first time.
The isolation of graphene in 2004 by a University of Manchester team lead by Sir Andre Geim and Sir Kostya Novoselov led to the discovery of a range of 2D materials, each with specific properties and qualities.
Dr Gorbachev said: "This is an important breakthrough in the area of 2D materials research, as it allows us to dramatically increase the variety of materials that we can experiment with using our expanding 2D crystal toolbox.
"The more materials we have to play with, the greater potential there is for creating applications that could revolutionise the way we live." Sir Andre Geim added:
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Daniel Cochlin
44-161-275-8382
Copyright © University of Manchester
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








