Home > Press > Flexible dielectric polymer can stand the heat
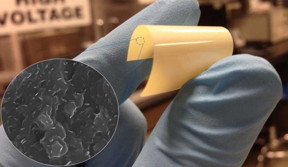 |
| Researcher holds flexible dielectric material. Pull out shows boron nitride nanosheets. CREDIT: Qing Wang, Penn State |
Abstract:
Easily manufactured, low cost, lightweight, flexible dielectric polymers that can operate at high temperatures may be the solution to energy storage and power conversion in electric vehicles and other high temperature applications, according to a team of Penn State engineers.
Flexible dielectric polymer can stand the heat
University Park, PA | Posted on August 6th, 2015"Ceramics are usually the choice for energy storage dielectrics for high temperature applications, but they are heavy, weight is a consideration and they are often also brittle," said Qing Wang, professor of materials science and engineering, Penn State. "Polymers have a low working temperature and so you need to add a cooling system, increasing the volume so system efficiency decreases and so does reliability."
Dielectrics are materials that do not conduct electricity, but when exposed to an electric field, store electricity. They can release energy very quickly to satisfy engine start-ups or to convert the direct current in batteries to the alternating current needed to drive motors.
Applications like hybrid and electric vehicles, aerospace power electronics and underground gas and oil exploration equipment require materials to withstand high temperatures. The researchers developed a cross-linked polymer nanocomposite containing boron nitride nanosheets. This material has high-voltage capacity for energy storage at elevated temperatures and can also be photo patterned and is flexible. The researchers report their results in a recent issue of Nature.
This boron nitride polymer composite can withstand temperatures of more than 480 degrees Fahrenheit under the application of high voltages. The material is easily manufactured by mixing the polymer and the nanosheets and then curing the polymer either with heat or light to create crosslinks. Because the nanosheets are tiny -- about 2 nanometers in thickness and 400 nanometers in lateral size, the material remains flexible, but the combination provides unique dielectric properties, which include higher voltage capability, heat resistance and bendability.
"Our next step is to try to make this material in large scale and put it into a real application," said Wang. "Theoretically, there is no exact scalability limit."
###
Also working on this project were Qi Li, Lei Chen and Guangu Zhang, postdoctoral Fellows; Matthew R. Gadinski, graduate student, materials science and engineering and Long-Qing Chen, distinguished professor of materials science and engineering and professor of engineering science and mechanics; Aman Haque, professor of mechanical engineering; Tom Jackson, Robert E. Kirby Chair Professor of Electrical Engineering and Haoyu Li, graduate student in electrical engineering; and Shihai Zhang, PolyK Technologies, State College. The researchers have filed a provisional patent disclosure on this work.
The Office of Naval Research, Air Force Office of Scientific Research and Dow Chemical Corporation supported this work.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
A'ndrea Elyse Messer
814-865-9481
Copyright © Penn State
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Automotive/Transportation
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Aerospace/Space
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








