Home > Press > Sandcastles inspire new nanoparticle binding technique
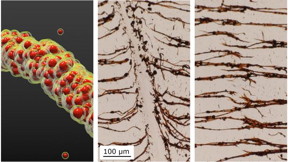 |
| NC State researchers develop a technique to assemble nanoparticles into filaments (left) in liquid. The filaments can be broken (middle) and then re-assembled (right). CREDIT: Image courtesy of Bhuvnesh Bharti. |
Abstract:
"Nanocapillary-mediated magnetic assembly of nanoparticles into ultraflexible filaments and reconfigurable networks"
Authors: Bhuvensh Bharti and Orlin D. Velev, North Carolina State University; Anne-Laure Fameau, National Institute of French Agricultural Research; Michael Rubenstein, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill
Published: Aug. 3, 2015, online in Nature Materials
DOI: 10.1038/nmat4364
Abstract: The fabrication of multifunctional materials with tunable structure and properties requires programmed binding of their building blocks. For example, particles organized in long-ranged structures by external fields can be bound permanently into stiff chains through electrostatic or van der Waals attraction, or into flexible chains through soft molecular linkers such as surface-grafted DNA or polymers. Here, we show that capillarity-mediated binding between magnetic nanoparticles coated with a liquid lipid shell can be used for the assembly of ultraflexible microfilaments and network structures. These filaments can be magnetically regenerated on mechanical damage, owing to the fluidity of the capillary bridges between nanoparticles and their reversible binding on contact. Nanocapillary forces offer opportunities for assembling dynamically reconfigurable multifunctional materials that could find applications as micromanipulators, microbots with ultrasoft joints, or magnetically self-repairing gels.
Sandcastles inspire new nanoparticle binding technique
Raleigh, NC | Posted on August 5th, 2015If you want to form very flexible chains of nanoparticles in liquid in order to build tiny robots with flexible joints or make magnetically self-healing gels, you need to revert to childhood and think about sandcastles.
In a paper published this week in Nature Materials, researchers from North Carolina State University and the University of North Carolina-Chapel Hill show that magnetic nanoparticles encased in oily liquid shells can bind together in water, much like sand particles mixed with the right amount of water can form sandcastles.
"Because oil and water don't mix, the oil wets the particles and creates capillary bridges between them so that the particles stick together on contact," said Orlin Velev, INVISTA Professor of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at NC State and the corresponding author of the paper.
"We then add a magnetic field to arrange the nanoparticle chains and provide directionality," said Bhuvnesh Bharti, research assistant professor of chemical and biomolecular engineering at NC State and first author of the paper.
Chilling the oil is like drying the sandcastle. Reducing the temperature from 45 degrees Celsius to 15 degrees Celsius freezes the oil and makes the bridges fragile, leading to breaking and fragmentation of the nanoparticle chains. Yet the broken nanoparticles chains will re-form if the temperature is raised, the oil liquefies and an external magnetic field is applied to the particles.
"In other words, this material is temperature responsive, and these soft and flexible structures can be pulled apart and rearranged," Velev said. "And there are no other chemicals necessary."
"This research was the result of collaboration initiated by the NSF Materials Research Science and Engineering Center that facilitates interactions between Triangle universities." said Michael Rubinstein, John P. Barker Distinguished Professor of Chemistry at UNC and one of the co-authors of the paper.
###
The paper is also co-authored by Anne-Laure Fameau, a visiting researcher from INRA, France. The research is funded by the National Science Foundation through the Triangle MRSEC on Programmable Soft Matter and the U.S. Army Research Office.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Dr. Orlin Velev
919-513-4318
Copyright © North Carolina State University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Robotics
![]() Nanofibrous metal oxide semiconductor for sensory face November 8th, 2024
Nanofibrous metal oxide semiconductor for sensory face November 8th, 2024
![]() Femtosecond laser technique births "dancing microrobots": USTC's breakthrough in multi-material microfabrication August 11th, 2023
Femtosecond laser technique births "dancing microrobots": USTC's breakthrough in multi-material microfabrication August 11th, 2023
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Molecular Nanotechnology
![]() Quantum pumping in molecular junctions August 16th, 2024
Quantum pumping in molecular junctions August 16th, 2024
![]() Scientists push the boundaries of manipulating light at the submicroscopic level March 3rd, 2023
Scientists push the boundaries of manipulating light at the submicroscopic level March 3rd, 2023
![]() First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








