Home > Press > Take a trip through the brain
 |
Abstract:
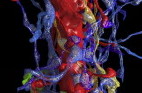
A new imaging tool developed by Boston scientists could do for the brain what the telescope did for space exploration. In the first demonstration of how the technology works, published July 30 in the journal Cell, the researchers look inside the brain of an adult mouse at a scale previously unachievable, generating images at a nanoscale resolution. The inventors' long-term goal is to make the resource available to the scientific community in the form of a national brain observatory.
Take a trip through the brain
Cambridge, MA | Posted on July 30th, 2015"I'm a strong believer in bottom up-science, which is a way of saying that I would prefer to generate a hypothesis from the data and test it," says senior study author Jeff Lichtman, of Harvard University. "For people who are imagers, being able to see all of these details is wonderful and we're getting an opportunity to peer into something that has remained somewhat intractable for so long. It's about time we did this, and it is what people should be doing about things we don't understand."
The researchers have begun the process of mining their imaging data by looking first at an area of the brain that receives sensory information from mouse whiskers, which help the animals orient themselves and are even more sensitive than human fingertips. The scientists used a program called VAST, developed by co-author Daniel Berger of Harvard and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, to assign different colors and piece apart each individual "object" (e.g., neuron, glial cell, blood vessel cell, etc.).
"The complexity of the brain is much more than what we had ever imagined," says study first author Narayanan "Bobby" Kasthuri, of the Boston University School of Medicine. "We had this clean idea of how there's a really nice order to how neurons connect with each other, but if you actually look at the material it's not like that. The connections are so messy that it's hard to imagine a plan to it, but we checked and there's clearly a pattern that cannot be explained by randomness."
The researchers see great potential in the tool's ability to answer questions about what a neurological disorder actually looks like in the brain, as well as what makes the human brain different from other animals and different between individuals. Who we become is very much a product of the connections our neurons make in response to various life experiences. To be able to compare the physical neuron-to-neuron connections in an infant, a mathematical genius, and someone with schizophrenia would be a leap in our understanding of how our brains shape who we are (or vice versa).
The cost and data storage demands for this type of research are still high, but the researchers expect expenses to drop over time (as has been the case with genome sequencing). To facilitate data sharing, the scientists are now partnering with Argonne National Laboratory with the hopes of creating a national brain laboratory that neuroscientists around the world can access within the next few years.
"It's bittersweet that there are many scientists who think this is a total waste of time as well as a big investment in money and effort that could be better spent answering questions that are more proximal," Lichtman says. "As long as data is showing you things that are unexpected, then you're definitely doing the right thing. And we are certainly far from being out of the surprise element. There's never a time when we look at this data that we don't see something that we've never seen before."
###
This work was supported by the NIH/NINDS, Conte, the MURI Army Research Office, the NSF, DARPA, the Human Frontier Science Program, the JHU Applied Physics Laboratory, the Research Program for Applied Neuroscience, the Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Nvidia, Intel, and Google.
####
About Cell Press
Cell, the flagship journal of Cell Press, is a bimonthly journal that publishes findings of unusual significance in any area of experimental biology, including but not limited to cell biology, molecular biology, neuroscience, immunology, virology and microbiology, cancer, human genetics, systems biology, signaling, and disease mechanisms and therapeutics.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Joseph Caputo
617-397-2802
Copyright © Cell Press
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Cell, Kasthuri et al.: "Saturated Reconstruction of a Volume of Neocortex":
Cell, Kasthuri et al.: "Saturated Reconstruction of a Volume of Neocortex":
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
Videos/Movies
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








