Home > Press > Researchers boost wireless power transfer with magnetic field enhancement
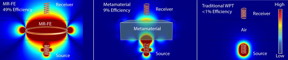 |
| From left to right are: performance of wireless power transfer using an MRFE, a metamaterial, and through air alone. CREDIT: David Ricketts |
Abstract:
Research from North Carolina State University and Carnegie Mellon University shows that passing wireless power transfer through a magnetic resonance field enhancer (MRFE) - which can be as simple as a copper loop - can boost the transfer efficiency by at least 100 percent as compared to transferring through air alone. MRFE use could potentially boost transfer efficiency by as much as 5,000 percent in some systems, experts say.
Researchers boost wireless power transfer with magnetic field enhancement
Raleigh, NC | Posted on July 23rd, 2015Wireless power transfer works by having a transmitter coil generate a magnetic field; a receiver coil then draws energy from that magnetic field. One of the major roadblocks for development of marketable wireless power transfer technologies is achieving high efficiency.
"Our experimental results show double the efficiency using the MRFE in comparison to air alone," says David Ricketts, an associate professor of electrical and computer engineering at NC State and corresponding author of a paper describing the work.
Enhancing wireless power efficiency has been a major goal of many research groups. One of the leading candidates proposed for enhancing efficiency has been a technology called metamaterials. "We performed a comprehensive analysis using computer models of wireless power systems and found that MRFE could ultimately be five times more efficient than use of metamaterials and 50 times more efficient than transmitting through air alone," Ricketts says.
By placing the MRFE between the transmitter and the receiver (without touching either) as an intermediate material, the researchers were able to significantly enhance the magnetic field, increasing its efficiency.
"We realized that any enhancement needs to not only increase the magnetic field the receiver 'sees,' but also not siphon off any of the power being put out by the transmitter," Ricketts says. "The MRFE amplifies the magnetic field while removing very little power from the system."
The researchers conducted an experiment that transmitted power through air alone, through a metamaterial, and through an MRFE made of the same quality material as the metamaterial. The MRFE significantly outperformed both of the others. In addition, the MRFE is less than one-tenth the volume of metamaterial enhancers.
"This could help advance efforts to develop wireless power transfer technologies for use with electric vehicles, in buildings, or in any other application where enhanced efficiency or greater distances are important considerations," Ricketts says.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Matt Shipman
919-515-6386
Copyright © North Carolina State University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Wireless/telecommunications/RF/Antennas/Microwaves
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Automotive/Transportation
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








