Home > Press > 3D-printed 'smart cap' uses electronics to sense spoiled food
 |
| UC Berkeley engineers created a "smart cap" using 3-D-printed plastic with embedded electronics to wirelessly monitor the freshness of milk. CREDIT: Photo by Sung-Yueh Wu |
Abstract:
It might not be long before consumers can just hit "print" to create an electronic circuit or wireless sensor in the comfort of their homes.
3D-printed 'smart cap' uses electronics to sense spoiled food
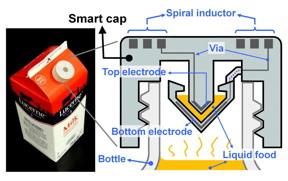
Berkeley, CA | Posted on July 20th, 2015Engineers at the University of California, Berkeley, in collaboration with colleagues at Taiwan's National Chiao Tung University, are expanding the already impressive portfolio of 3D printing technology to include electrical components, such as resistors, inductors, capacitors and integrated wireless electrical sensing systems. They have put the new technology to the test by printing a wireless "smart cap" for a milk carton that detected signs of spoilage using embedded sensors.
The findings are to be published Monday, July 20, in a new open-access journal in the Nature Publishing Group called Microsystems & Nanoengineering.
Major advances over the past 10 years have enabled the creation of a wide array of 3D-printed products, including prosthetics, medical implants, toys, vehicle parts, building materials and even food. What had been missing from the repertoire until now was the ability to produce sensitive electronic components.
"Our paper describes the first demonstration of 3D printing for working basic electrical components, as well as a working wireless sensor," said senior author Liwei Lin, a professor of mechanical engineering and co-director of the Berkeley Sensor and Actuator Center. "One day, people may simply download 3D-printing files from the Internet with customized shapes and colors and print out useful devices at home."
Polymers are attractive materials in the world of 3D printing because their flexibility allows them to be formed into a variety of shapes. However, such materials are poor conductors of electricity, and thus bad candidates for electronic devices. To get around this, the researchers started off by building a system using polymers and wax. They would then remove the wax, leaving hollow tubes into which liquid metal - in their experiments they used silver - was injected and then cured.
The shape and design of the metal determined the function of different electrical components. For instance, thin wires acted as resistors, and flat plates were made into capacitors. But the question remained: Do the pieces of metal actually do anything useful?
To answer that, the researchers integrated the electronic components into a plastic milk carton cap to monitor signs of spoilage. The "smart cap" was fitted with a capacitor and an inductor to form a resonant circuit. A quick flip of the carton allowed a bit of milk to get trapped in the cap's capacitor gap, and the entire carton was then left unopened at room temperature (about 71.6 degrees Fahrenheit) for 36 hours.
The circuit could detect the changes in electrical signals that accompany increased levels of bacteria. The researchers periodically monitored the changes with a wireless radio-frequency probe at the start of the experiment and every 12 hours thereafter, up to 36 hours. The property of milk changes gradually as it degrades, leading to variations in its electrical characteristics. Those changes were detected wirelessly using the smart cap, which found that the peak vibration frequency of the room-temperature milk dropped by 4.3 percent after 36 hours. In comparison, a carton of milk kept in refrigeration at 39.2 degrees Fahrenheit saw a relatively minor 0.12 percent shift in frequency over the same time period.
"This 3D-printing technology could eventually make electronic circuits cheap enough to be added to packaging to provide food safety alerts for consumers," said Lin. "You could imagine a scenario where you can use your cellphone to check the freshness of food while it's still on the store shelves."
As 3D printers become cheaper and better, the options for electronics will expand, said Lin, though he does not think people will be printing out their own smartphones or computers anytime soon.
"That would be very difficult because of the extremely small size of modern electronics," he said. "It might also not be practical in terms of price since current integrated circuits are made by batch fabrication to keep costs low. Instead, I see 3D-printed microelectronic devices as very promising for systems that would benefit from customization."
Lin said his lab is working on developing this technology for health applications, such as implantable devices with embedded transducers that can monitor blood pressure, muscle strain and drug concentrations.
###
The co-lead authors of the study are UC Berkeley research specialist Chen Yang and visiting Ph.D. student Sung-Yueh Wu, both working in Lin's lab. Wu is also a student of study co-author Wensyang Hsu, a professor of mechanical engineering at National Chiao Tung University.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Sarah Yang
510-643-7741
Copyright © University of California, Berkeley
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
3D & 4D printing/Additive-manufacturing
![]() Presenting: Ultrasound-based printing of 3D materials—potentially inside the body December 8th, 2023
Presenting: Ultrasound-based printing of 3D materials—potentially inside the body December 8th, 2023
![]() Fiber sensing scientists invent 3D printed fiber microprobe for measuring in vivo biomechanical properties of tissue and even single cell February 10th, 2023
Fiber sensing scientists invent 3D printed fiber microprobe for measuring in vivo biomechanical properties of tissue and even single cell February 10th, 2023
![]() 3D-printed decoder, AI-enabled image compression could enable higher-res displays December 9th, 2022
3D-printed decoder, AI-enabled image compression could enable higher-res displays December 9th, 2022
![]() Researchers design new inks for 3D-printable wearable bioelectronics: Potential uses include printing electronic tattoos for medical tracking applications August 19th, 2022
Researchers design new inks for 3D-printable wearable bioelectronics: Potential uses include printing electronic tattoos for medical tracking applications August 19th, 2022
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Food/Agriculture/Supplements
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() SMART researchers pioneer first-of-its-kind nanosensor for real-time iron detection in plants February 28th, 2025
SMART researchers pioneer first-of-its-kind nanosensor for real-time iron detection in plants February 28th, 2025
![]() Silver nanoparticles: guaranteeing antimicrobial safe-tea November 17th, 2023
Silver nanoparticles: guaranteeing antimicrobial safe-tea November 17th, 2023
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








