Home > Press > Caught on camera: The first glimpse of powerful nanoparticles
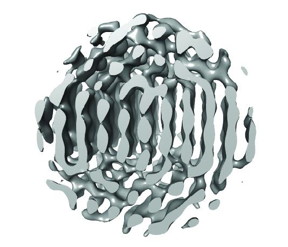 |
| This a slab through the 3-D reconstruction of particle 1 along the vertical plane with tentative atomic positions indicated. ABC repeats of {111} planes are visible. CREDIT: ARC Centre of Excellence in Advanced Molecular Imaging |
Abstract:
Researchers have developed a new method to capture the 3D structures of nanocrystals. Scientists believe these tiny particles could be used to fight cancer, collect renewable energy and mitigate pollution.
Caught on camera: The first glimpse of powerful nanoparticles
Victoria, Australia | Posted on July 17th, 2015Metallic nanoparticles are some of the smallest particles. Their dimensions are measured in nanometres, with each nanometre being one millionth of a milimetre. Until now, it has been difficult to know how they work, because they are so small their structure is impossible to see.
The novel imaging method, developed by an international team from the US, Korea and Australia will allow researchers to investigate the 3D structure of these miniscule particles for the first time.
The research, published today in Science, was co-led by Associate Professor Hans Elmlund from the ARC Centre of Excellence in Advanced Molecular Imaging based at Monash University. The work, performed in collaboration with researchers from Princeton, Boston and Harvard Universities, reveals the details of the method and shows how it can be used to characterise the 3D structures of these miniscule particles for the first time.
The method is called "3D Structure Identification of Nanoparticles by Graphene Liquid Cell EM (SINGLE)" and it exceeds previous techniques by combining three recently developed components.
The first is a graphene liquid cell, a bag one molecule thick that can hold liquid inside it while being exposed to the ultra high vacuum of the electron microscope column. The second is a direct electron detector, which is even more sensitive than traditional camera film and can be used to capture movies of the nanoparticles as they spin around in solution. Finally, a 3D modeling approach known as PRIME allows use of the movies to create three-dimensional computer models of individual nanoparticles.
Movie clips that accompany the publication capture the structure of two platinum nanoparticles, which have never been seen in such detail before. Elmlund and his colleagues were able to draw new conclusions about how these highly useful particles grow at the level of individual atoms.
The field had anticipated cubical or at least highly symmetrical platinum nanocrystals.
"It was surprising to learn that they form asymmetrical multi-domain structures," Elmlund said.
The next steps in the project will include investigating the formation and evolution of nanoparticles and characterising the transitions they go through to reach their final form. "It is important for us to understand this, so that we can design new materials, for example, to build better or more efficient solar cells, or make better and more economical use of fossil fuels," Elmlund said.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Monash Media Team
Copyright © Monash University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Videos/Movies
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
![]() Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








