Home > Press > Tunneling out of the surface
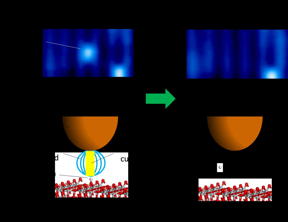 |
| Figure 1 shows the manipulation of an atomic defect using the probe of a scanning tunneling microscope. CREDIT: ACS Nano |
Abstract:
A research team comprising scientists from Tohoku University, RIKEN, the University of Tokyo, Chiba University and University College London have discovered a new chemical reaction pathway on titanium dioxide (TiO2), an important photocatalytic material.
Tunneling out of the surface
Sendai, Japan | Posted on July 9th, 2015The reaction mechanism, reported in ACS Nano, involves the application of an electric field that narrows the width of the reaction barrier, thereby allowing hydrogen atoms to tunnel away from the surface. This opens the way for the manipulation of the atomic-scale transport channels of hydrogen, which could be important in hydrogen storage. Hydrogen has been put forward as a clean and renewable alternative to the burning of hydrocarbons and one of the great challenges of our day is to find an efficient way to store and transport it.
The team used scanning tunneling microscopy (STM) to directly visualize single hydrogen ions, a common atomic defect on TiO2 (Fig. 1). In STM, the surface structure of a solid surface is observed on the atomic scale by scanning a sharp probe across the surface and monitoring the tunneling current. Minato et al. were able to desorb individual hydrogen ions from the surface by using the STM probe to apply electrical pulses to the hydrogen. The pulse generates an electric field as well as injecting electrons into the sample. By using a new theoretical approach developed by Dr. Kajita, the team confirmed that rather than reducing the reaction barrier height, the electric field reduces the width of the barrier, thereby allowing the hydrogen to desorb by quantum tunneling (Fig. 2).
Lead author Prof. Taketoshi Minato (Tohoku Univ. and RIKEN, currently Kyoto University) commented that "The new reaction pathway could be exploited in nanoscale switching devices and hydrogen storage technology. For instance, electric fields could be used to extract hydrogen from a TiO2-based storage device"
###
Publication Details
Authors: Taketoshi Minato, Seiji Kajita, Chi-Lun Pang, Naoki Asao, Yoshinori Yamamoto, Takashi Nakayama, Maki Kawai, and Yousoo Kim
Title: Tunneling Desorption of Single Hydrogen on the Surface of Titanium Dioxide
Journal: ACS Nano (American Chemical Society)
DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.5b01607
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Professor Taketoshi Minato
International Advanced Research and Education Organization
Office of Society-Academia Collaboration for Innovation
Kyoto University
Tel: +81-774-38-4942
(Formerly of Tohoku University and RIKEN)
Dr. Yousoo Kim
Surface and Interface Science Laboratory, RIKEN
Tel: +81-48?467?4073
Professor Maki Kawai
Department of Advanced Materials Science
The University of Tokyo
Tel: +81-4-7136-3787
Dr. Seiji Kajita
Toyota Central R&D Labs, Inc.
Tel: +81-561-71-7258
(Formerly of Chiba University)
Dr. Chi-Lun Pang
Department of Chemistry, University College London
Tel: +44-207-679-5580
Copyright © Tohoku University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








