Home > Press > Building a better semiconductor: Research led by Michigan State University could someday lead to the development of new and improved semiconductors
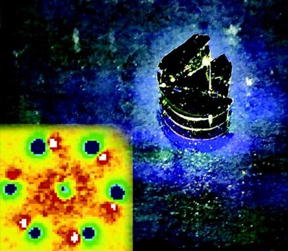 |
| MSU researchers have found that by shooting an ultrafast laser pulse into a material, it can change its properties, a process that can lead to the development of new and improved semiconductors. The image on the right is an illustrated view of a material irradiated by the laser pulses. The one of the left is an image of the material showing subtle structural changes as a result of what’s known as photo-doping. Photo courtesy of the MSU Department of Physics and Astronomy. |
Abstract:
In a paper published in the journal Science Advances, the scientists detailed how they developed a method to change the electronic properties of materials in a way that will more easily allow an electrical current to pass through.
Building a better semiconductor: Research led by Michigan State University could someday lead to the development of new and improved semiconductors
East Lansing, MI | Posted on June 27th, 2015The electrical properties of semiconductors depend on the nature of trace impurities, known as dopants, which when added appropriately to the material will allow for the designing of more efficient solid-state electronics.
The MSU researchers found that by shooting an ultrafast laser pulse into the material, its properties would change as if it had been chemically "doped." This process is known as "photo-doping."
"The material we studied is an unconventional semiconductor made of alternating atomically thin layers of metals and insulators," said Chong-Yu Ruan, an associate professor of physics and astronomy who led the research effort at MSU. "This combination allows many unusual properties, including highly resistive and also superconducting behaviors to emerge, especially when 'doped.'"
An ultrafast electron-based imaging technique developed by Ruan and his team at MSU allowed the group to observe the changes in the materials. By varying the wavelengths and intensities of the laser pulses, the researchers were able to observe phases with different properties that are captured on the femtosecond timescale. A femtosecond is 1 quadrillionth, or 1 millionth of 1 billionth, of a second.
"The laser pulses act like dopants that temporarily weaken the glue that binds charges and ions together in the materials at a speed that is ultrafast and allow new electronic phases to spontaneously form to engineer new properties," Ruan said. "Capturing these processes in the act allows us to understand the physical nature of transformations at the most fundamental level."
Philip Duxbury, a team member and chairperson of the department of physics and astronomy, said ultrafast photo-doping "has potential applications that could lead to the development of next-generation electronic materials and possibly optically controlled switching devices employing undoped semiconductor materials."
A semiconductor is a substance that conducts electricity under some conditions but not others, making it a good medium for the control of electrical current. They are used in any number of electronics, including computers.
###
Other collaborators on the project include the research group of S.D. Mahanti, professor of physics and astronomy at MSU, and the Mercouri Kanatzidis research group at Northwestern University.
The research is supported by Basic Energy Sciences, U.S. Department of Energy.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Tom Oswald
517-432-0920
Copyright © Michigan State University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Hardware
![]() The present and future of computing get a boost from new research July 21st, 2023
The present and future of computing get a boost from new research July 21st, 2023
![]() A Carbon Nanotube Microprocessor Mature Enough to Say Hello: Three new breakthroughs make commercial nanotube processors possible March 2nd, 2020
A Carbon Nanotube Microprocessor Mature Enough to Say Hello: Three new breakthroughs make commercial nanotube processors possible March 2nd, 2020
![]() Powering the future: Smallest all-digital circuit opens doors to 5 nm next-gen semiconductor February 11th, 2020
Powering the future: Smallest all-digital circuit opens doors to 5 nm next-gen semiconductor February 11th, 2020
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








