Home > Press > Nanoparticles naturally fall into left- and right-handed versions
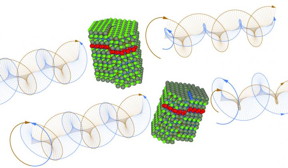 |
| These are levorotatory and dextrorotatory quantum dots with left and right chiral defects. CREDIT: Courtesy of ITMO University |
Abstract:
A team of scientists from ITMO University and Trinity College Dublin published first experimental results showing that ordinary nanocrystals possess intrinsic chirality and can be produced under normal conditions as a half-and-half mixture of mirror images of each other. The discovery of this fundamental property in nanocrystals opens new horizons in nano- and bio-technology and medicine, for instance, for such applications as targeted drug delivery. The results of the study were published in Nano Letters.
Nanoparticles naturally fall into left- and right-handed versions
St. Petersburg, Russia | Posted on June 16th, 2015Ever since the development of artificial nanocrystals, scientists thought that chirality -- the property of an object to be non-superimposable with its mirror image -- was either random or completely absent in nanocrystals.
A joint experiment conducted by researchers from Optics of Quantum Nanostructures laboratory at ITMO University and Centre for Research on Adaptive Nanostructures and Nanodevices (CRANN) at Trinity College has demonstrated that standard nanocrystals (cadmium selenide quantum dots and quantum rods), in fact, make up a racemic (50:50) mixture of 'right' and 'left' chiral forms. Until now, chiral nanocrystals could only be achieved artificially by attaching special chiral ligand molecules to the surface of nanocrystals.
Chirality is intrinsic to many objects of the natural world, starting from elementary particles to spiral galaxies. Our body, as well as many other complex biological objects, is almost entirely made of chiral biomolecules. Importantly, the biological activity of 'right' and 'left' forms of the same compound might differ dramatically. Often only one chiral form is edible or has the required therapeutic effect, while its antipode will be at best useless. For example, molecules of a well-known painkiller ibuprofen have two optical mirror isomers. One of them indeed helps relieve pain, while the other not only does not relieve pain, but is toxic for the organism.
A key indicator of chiral environment is called optical activity: depending on the chiral form of a nanocrystal, it can rotate the plane of polarized light either to the right or to the left. A normal solution of nanocrystals by definition does not reveal any optical activity, which was always attributed to the apparent inexistence of chirality in nanocrystals. Having divided 'left' and 'right' forms of nanocrystals, scientists from ITMO University and Trinity College managed to prove the opposite.
'The absence of optical activity in a solution of nanocrystals can be explained by the fact that a racemic (50:50) mixture combines 'left' and 'right' versions of nanocrystals that simultaneously rotate the plane of polarization in opposite directions, thus cancelling each other out,' says Maria Mukhina, researcher at Optics of Quantum Nanostructures laboratory. 'We explain the very existence of intrinsic chirality in nanocrystals by chiral defects that occur naturally during normal synthesis of nanocrystals.'
Yurii Gun'ko, professor at Trinity College and co-director of International Research and Education Centre for Physics of Nanostructures at ITMO University comments on potential applications of the method developed by the group:
'There is a global demand for new ways of obtaining chiral nanoparticles. We believe that our method will find applications in biopharmaceutics, nanobiotechnology, nanotoxicology and biomedicine, in particular for medical diagnostics and targeted drug delivery. For example, if all commonly used nanoparticles are indeed chiral, then during interaction with a biological object 50 percent of nanoparticle mixture will penetrate into the biological object (e.g. cell), while the other 50 percent will remain outside. The implications of this conclusion are crucial for nanotoxicology area, but nobody considered them before. Another potential application has to do with the ability of chiral quantum dots to emit levorotatory and dextrorotatory polarized light, which makes it possible to create devices such as 3-D holographic displays and much more.'
To separate different chiral forms of nanocrystals and capture the manifestation of their intrinsic chirality, the scientists came up with a technique that, according to the group, can be potentially expanded and used with many other inorganic nanomaterials.
The researchers immersed nanocrystals in a two-phase unmixable solution of water and organic solvent (chloroform). As nanocrystals are not soluble in water, in order to transfer them from organic phase to water, scientists added L-cysteine, a chiral molecule frequently used as a ligand for such a phase transfer. Cysteine replaces hydrophobic ligands on the surface of nanocrystals making the latter water-soluble. As a result, regardless of the chiral form of cysteine, all nanocrystals without exception will end up in water. Researchers found that if they cool the solution and interrupt the phase transfer at a certain point, it is possible to achieve a situation, wherein the ensemble of nanocrystals is divided equally between the phases with 'left' and 'right' nanocrystals in different phases.
Optical activity in nanocrystals separated in this way is preserved even after the subsequent removal of cysteine from the surface, which additionally testifies to the natural origin of intrinsic chirality in nanocrystals.
###
Publication:
'Intrinsic chirality of CdSe/ZnS quantum dots and quantum rods,' Maria V. Mukhina, Vladimir G. Maslov, Alexander V. Baranov, Anatoly V. Fedorov, Anna O. Orlova, Finn Purcell-Milton, Joseph Govan, and Yurii K. Gun'ko, Nano Letters., 2015, 15 (5), pp 2844-2851DOI: 10.1021/nl504439w.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Dmitry Malkov
7-953-377-5508
Copyright © ITMO University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
Chemistry
![]() Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








