Home > Press > Strong teeth: Nanostructures under stress make teeth crack resistant
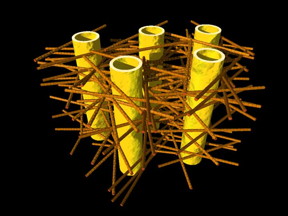 |
| Illustration shows complex biostructure of dentin: the dental tubuli (yellow hollow cylinders, diameters appr. 1 micrometer) are surrounded by layers of mineralized collagen fibers (brown rods). The tiny mineral nanoparticles are embedded in the mesh of collagen fibers and not visible here. Credit: JB Forien @Charité |
Abstract:
Human teeth have to serve for a lifetime, despite being subjected to huge forces. But the high failure resistance of dentin in teeth is not fully understood. An interdisciplinary team led by scientists of Charite Universitaetsmedizin Berlin has now analyzed the complex structure of dentin. At the synchrotron sources BESSY II at HZB, Berlin, Germany, and the European Synchrotron Radiation Facility ESRF, Grenoble, France, they could reveal that the mineral particles are precompressed.
Strong teeth: Nanostructures under stress make teeth crack resistant
Berlin, Germany | Posted on June 10th, 2015The internal stress works against crack propagation and increases resistance of the biostructure.
Engineers use internal stresses to strengthen materials for specific technical purposes. Now it seems that evolution has long 'known' about this trick, and has put it to use in our natural teeth. Unlike bones, which are made partly of living cells, human teeth are not able to repair damage. Their bulk is made of dentin, a bonelike material consisting of mineral nanoparticles. These mineral nanoparticles are embedded in collagen protein fibres, with which they are tightly connected. In every tooth, such fibers can be found, and they lie in layers, making teeth tough and damage resistant. Still, it was not well understood, how crack propagation in teeth can be stopped.
Now researchers from Charite Julius-Wolff-Institute, Berlin have been working with partners from Materials Engineering Department of Technische Universitaets Berlin, MPI of Colloids and Interfaces, Potsdam and Technion - Israel Institute of Technology, Haifa, to examine these biostructures more closely. They performed Micro-beam in-situ stress experiments in the mySpot BESSY facility of HZB, Berlin, Germany and analyzed the local orientation of the mineral nanoparticles using the nano-imaging facility of the European Synchrotron Radiation Facility (ESRF) in Grenoble, France.
When the tiny collagen fibers shrink, the attached mineral particles become increasingly compressed, the science team found out. "Our group was able to use changes in humidity to demonstrate how stress appears in the mineral in the collagen fibers, Dr. Paul Zaslansky from Julius Wolff-Institute of Charite Berlin explains. "The compressed state helps to prevents cracks from developing and we found that compression takes place in such a way that cracks cannot easily reach the tooth inner parts, which could damage the sensitive pulp. In this manner, compression stress helps to prevent cracks from rushing through the tooth.
The scientists also examined what happens if the tight mineral-protein link is destroyed by heating: In that case, dentin in teeth becomes much weaker. We therefore believe that the balance of stresses between the particles and the protein is important for the extended survival of teeth in the mouth, Charite scientist Jean-Baptiste Forien says. Their results may explain why artificial tooth replacements usually do not work as well as healthy teeth do: they are simply too passive, lacking the mechanisms found in the natural tooth structures, and consequently fillings cannot sustain the stresses in the mouth as well as teeth do. "Our results might inspire the development of tougher ceramic structures for tooth repair or replacement, Zaslansky hopes.
Experiments took place as part of the DFG project "Biomimetic Materials Research: Functionality by Hierarchical Structuring of Materials (SPP1420).
###
The results are published in Nanoletters, DOI: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.5b00143
DOI: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.5b00143 Jean-Baptiste Forien, Claudia Fleck, Peter Cloetens, Georg Duda, Peter Fratzl, Emil Zolotoyabko, Paul Zaslansky. Compressive Residual Strains in Mineral Nanoparticles as a Possible Origin of Enhanced Crack Resistance in Human Tooth Dentin. Nano Letters. 2015 May 29.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Dr. Paul Zaslansky
49-304-505-59589
Copyright © Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin für Materialien und Energie
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Dental
![]() Innovations in dentistry: Navigational surgery, robotics, and nanotechnology October 2nd, 2020
Innovations in dentistry: Navigational surgery, robotics, and nanotechnology October 2nd, 2020
![]() First measurement of electron energy distributions, could enable sustainable energy technologies June 5th, 2020
First measurement of electron energy distributions, could enable sustainable energy technologies June 5th, 2020
![]() Gas storage method could help next-generation clean energy vehicles: Tremendous amounts of hydrogen and methane can be stored in nanoscopic pores April 17th, 2020
Gas storage method could help next-generation clean energy vehicles: Tremendous amounts of hydrogen and methane can be stored in nanoscopic pores April 17th, 2020
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








