Home > Press > Seeing the action: UCSB researchers develop a novel device to image the minute forces and actions involved in cell membrane hemifusion
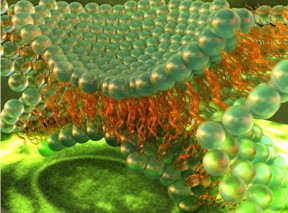 |
| This is an artist's concept of cell hemifusion. CREDIT: Peter Allen |
Abstract:
Cells are biological wonders. Throughout billions of years of existence on Earth, these tiny units of life have evolved to collaborate at the smallest levels in promoting, preserving and protecting the organism they comprise. Among these functions is the transport of lipids and other biomacromolecules between cells via membrane adhesion and fusion -- processes that occur in many biological functions, including waste transport, egg fertilization and digestion.
Seeing the action: UCSB researchers develop a novel device to image the minute forces and actions involved in cell membrane hemifusion
Santa Barbara, CA | Posted on May 27th, 2015At the University of California, Santa Barbara, chemical engineers have developed a way to directly observe both the forces present and the behavior that occurs during cell hemifusion, a process by which only the outer layers of the lipid bilayer of cell membranes merge. While many different techniques have been used to observe membrane hemifusion, simultaneous measurements of membrane thickness and interaction forces present a greater challenge, according to Dong Woog Lee, lead author of a paper that appears in the journal Nature Communications.
'It is hard to simultaneously image hemifusion and measure membrane thickness and interaction forces due to the technical limitations,' he said.
However, by combining the capabilities of the Surface Forces Apparatus (SFA) -- a device that can measure the tiny forces generated by the interaction of two surfaces at the sub-nano scale -- and simultaneous imaging using a fluorescence microscope, the researchers were able to see in real time how the cell membranes rearrange in order to connect and open a fusion conduit between them. The SFA was developed in Professor Jacob Israelachvili's Interfacial Sciences Lab at UCSB. Israelachvili is a faculty member in the Department of Chemical Engineering at UCSB.
To capture real time data on the behavior of cell membranes during hemifusion, the researchers pressed together two supported lipid bilayers on the opposing surfaces of the SFA. These bilayers consisted of lipid domains -- collections of lipids that in non-fusion circumstances are organized in more or less regularly occurring or mixed arrangements within the cell membrane.
'We monitored these lipid domains to see how they reorganize and relocate during hemifusion,' said Lee. The SFA measured the forces and distances between the two membrane surfaces as they were pushed together, visualized at the Ångstrom (one-tenth of a nanometer) level. Meanwhile, fluorescent imaging made it possible to see the action as the more ordered-phase (more solid) domains reorganized and allowed the more disordered-phase (more fluid) domains to concentrate at the point of contact.
'This is the first time observing fluorescent images during a hemifusion process simultaneously with how the combined thickness of the two bilayers evolve to form a single layer,' said Lee. This rearrangement of the domains, he added, lowers the amount of energy needed during the many processes that require membrane fusion. At higher pressures, according to the study, the extra energy activates faster hemifusion of the lipid layers.
Lipid domains have been seen in many biological cell membranes, and have been linked to various diseases such as multiple sclerosis, Alzheimer's disease and lung diseases. According to the researchers, this novel device could be used to diagnose, provide a marker for, or study dynamic transformations in situations involving lipid domains in pathological membranes. The fundamental insights provided by this device could also prove useful for other materials in which dynamic changes occur between membranes, including surfactant monolayers and bilayers, biomolecules, colloidal particles, surfactant-coated nanoparticles and smart materials.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Sonia Fernandez
805-893-4765
Copyright © University of California - Santa Barbara
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








