Home > Press > Quantum model reveals surface structure of water: National Physical Laboratory, IBM and Edinburgh University have used a new quantum model to reveal the molecular structure of water's liquid surface
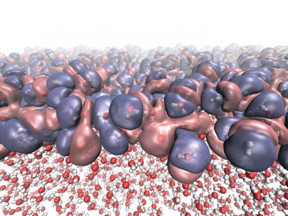 |
| This shows the heterogeneous electronic density created by the diverse molecular orientations at the liquid-vapor interface of water. CREDIT: NPL/University of Edinburgh |
Abstract:
The National Physical Laboratory (NPL), the UK's National Measurement Institute in collaboration with IBM and the University of Edinburgh, has used a new quantum model to reveal the molecular structure of water's liquid surface.
Quantum model reveals surface structure of water: National Physical Laboratory, IBM and Edinburgh University have used a new quantum model to reveal the molecular structure of water's liquid surface
Teddington, UK | Posted on April 20th, 2015The liquid-vapour interface of water is one of the most common of all heterogeneous (or non-uniform) environments. Understanding its molecular structure will provide insight into complex biochemical interactions underpinning many biological processes. But experimental measurements of the molecular structure of water's surface are challenging, and currently competing models predict various different arrangements.
NPL has been working with IBM and the University of Edinburgh to make materials simulation more predictive and intuitive, by developing a new class of materials model based on quantum mechanical effects.
The model is based on a single charged particle, the quantum Drude oscillator (QDO), which mimics the way the electrons of a real water molecule fluctuate and respond to their environment. This simplified representation retains interactions not normally accessible in classical models and accurately captures the properties of liquid water.
In new research, published in a featured article in the journal Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, the team used the QDO model to determine the molecular structure of water's liquid surface. The results provide new insight into the hydrogen-bonding topology at the interface, which is responsible for the unusually high surface tension of water.
This is the first time the QDO model of water has been applied to the liquid-vapour interface. The results enabled the researchers to identify the intrinsic asymmetry of hydrogen bonds as the mechanism responsible for the surface's molecular orientation. The model was also capable of predicting the temperature dependence of the surface tension with remarkable accuracy - to within 1 % of experimental values.
Coupled with earlier work on bulk water, this result demonstrates the exceptional transferability of the QDO approach and offers a promising new platform for molecular exploration of condensed matter.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Joe Meaney
44-787-546-9309
Copyright © National Physical Laboratory (NPL)
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Water
![]() Taking salt out of the water equation October 7th, 2022
Taking salt out of the water equation October 7th, 2022
Quantum nanoscience
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








