Home > Press > Light in a spin: Researchers demonstrate angular accelerating light
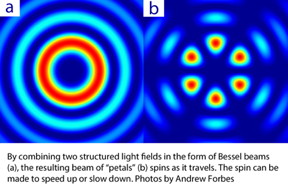 |
Abstract:
Light must travel in a straight line and at a constant speed, or so the laws of nature suggest. Now, researchers at the University of the Witwatersrand in Johannesburg have demonstrated that laser light traveling along a helical path through space, can accelerate and decelerate as it spins into the distance.
Light in a spin: Researchers demonstrate angular accelerating light
Johannesburg, South Africa | Posted on April 15th, 2015This is the first time that angular acceleration has been observed with light, and is therefore likely to lead to new applications using these structured light fields.
The results are contained in a research paper by Professor Andrew Forbes from the Wits School of Physics and his collaborators¹, published online this week in the journal, Physical Review A. Titled: Accelerated rotation with orbital angular momentum modes, the work has also been selected as a highlighted paper by the editors.
Forbes, who joined the Wits School of Physics in March this year, is heading up the new Structured Light Laboratory that focuses on creating custom light fields using digital holograms. The research group creates complex light that exhibits interesting physical properties, which they exploit for a range of applications.
Previously, Forbes and his collaborators have shown that light could be made to spin. In this recent work they demonstrated the first realisation of angular accelerating light and showed that light could also be made to accelerate and decelerate. This acceleration can be controlled with a single parameter that is readily tuned with a digital hologram written to a standard LCD screen, much like your LCD television at home, but just a much smaller version.
"Our angular accelerating fields rely on combinations of orbital angular momentum - so-called twisted light," says Forbes. Light carrying orbital angular momentum is created by twisting the wave-front of light into a helical shape, forming a spiral. Usually this twist in the light's wave-front is smooth, like a spiral staircase with regular steps. "Our novelty was to realise that by twisting the helicity of these beams in a non-linear fashion, the result would be a propagation dependent angular velocity," he explains. In other words, the light spins at a non-constant speed, resulting in angular acceleration.
In fact, the light speeds up and slows down as it travels, periodically switching from one mode to the other. Following its helical path through space, the helix appears to wind up very tightly as it accelerates, and winds down very loosely as it decelerates. It is intriguing that by "twisting the twist", nature provides an additional momentum to the field causing it to accelerate as it spins.
The team expects this new optical field to be of interest as a tool to study some fundamental physical processes with light, as well as a tool in optically driving micro-fluidic flow.
###
¹The idea was conceived by Forbes who led the collaboration with Christian Schulze and Michael Duparré (University of Jena, Germany), Ronald Rop (Eggerton University, Kenya), and Filippus Roux and Angela Dudley (Council for Scientific and Industrial Research, South Africa).
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Erna van Wyk
27-117-174-023
Copyright © University of the Witwatersrand
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
Microfluidics/Nanofluidics
![]() Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Display technology/LEDs/SS Lighting/OLEDs
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Videos/Movies
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








