Home > Press > A new breakthrough in thermoelectric materials
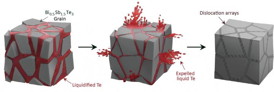 |
| This schematic illustration shows the generation of dislocation arrays during the liquid-phase compaction process. The Te liquid (red) between the Bi0.5Sb1.5Te3 grains flows out during the compacting process and facilitates the formation of dislocation arrays embedded in low-energy grain boundaries.
CREDIT: Institute for Basic Science |
Abstract:
French physicist Jean Charles Athanase Peltier discovered a key concept necessary for thermoelectric (TE) temperature control in 1834. His findings were so significant, TE devices are now commonly referred to Peltier devices. Since his work, there have been steady advancements in materials and design. Despite the technological sophistication Peltier devices, they are still less energy efficient than traditional compressor/evaporation cooling.
A new breakthrough in thermoelectric materials
Daejeon, Korea | Posted on April 2nd, 2015In the 1960's, Peltier devices were primarily made from Bismuth-Telluride (Bi2Te3) or Antimony-Telluride (Sb2Te3) alloys and had a peak efficiency (zT) of 1.1, meaning the electricity going in was only slightly less than the heat coming out. Since the 1960's there have been incremental advancements in alloy technology used in Peltier devices.
In 2014, researchers in South Korea at IBS Center for Integrated Nanostructure Physics along with Samsung Advanced Institute of Technology, the Department of Nano Applied Engineering at Kangwon National University, the Department of Energy Science at Sungkyunkwan University, and Materials Science department at California Institute of Technology California, USA have formulated a new method for creating a novel and much more efficient TE alloy.
TE alloys are special because the metals have an incredibly high melting point. Instead of melting the metals to fuse them, they are combined through a process called sintering which uses heat and/or pressure to join the small, metallic granules. The joint team, including IBS researchers, used a process called liquid-flow assisted sintering which combined all three antimony, bismuth and telluride granules into one alloy (Bi0.5Sb1.5Te3). Additional melted tellurium was used as the liquid between the Bi0.5Sb1.5Te3 granules to help fuse them into a solid alloy, and excess Te is expelled in the process.
By creating the alloy this way, the joints between the fused grains, also known as the grain boundaries, took on a special property. Traditionally sintered Bi0.5Sb1.5Te3 have thick, coarse joints which have led to a decrease in both thermal and electrical conductivity. The new liquid-phase sintering creates grain boundaries which are organized and aligned in seams called dislocation arrays. These dislocation arrays greatly reduce their thermal conduction, leading to an enhancement of their thermoelectric conversion efficiency.
In tests, the efficiency (zT) reached 2.01 at 320 K within the range of 1.86 ±0.15 at 320 K (46.85° C) for 30 samples, nearly doubling the industry standard. When the melt spun Bi0.5Sb1.5Te3 alloy is used in a Peltier cooler, the results are also significant. The new material was able achieve a temperature change of 81 K at 300 K (26.85° C).
The applications for such a material are abundant. As new fabrication techniques are developed, Peltier cooling devices may be used in place of traditional compression refrigeration systems. More importantly, as electrical vehicles and personal electronic devices become more ubiquitous in our daily lives, it is becoming increasingly necessary to have more efficient systems for localized electrical power generation and effective cooling mechanisms. This new thermoelectric alloy paves the way for the future of modern TE devices.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Sunny Kim
Copyright © Institute for Basic Science (IBS)
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








