Home > Press > Wrapping carbon nanotubes in polymers enhances their performance: Scientists at Japan's Kyushu University say polymer-wrapped carbon nanotubes hold much promise in biotechnology and energy applications
 |
Abstract:
Scientists first reported carbon nanotubes in the early 1990s. Since then, these tiny cylinders have been part of the quest to reduce the size of technological devices and their components. Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) have very desirable properties. They are 100 times stronger than steel and one-sixth its weight. They have several times the electrical and thermal conductivity of copper. And they have almost none of the environmental or physical degradation issues common to most metals, such as thermal contraction and expansion or erosion.
Wrapping carbon nanotubes in polymers enhances their performance: Scientists at Japan's Kyushu University say polymer-wrapped carbon nanotubes hold much promise in biotechnology and energy applications
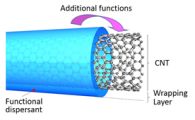
Tsukuba, Japan | Posted on March 30th, 2015CNTs have a tendency to aggregate, forming "clumps" of tubes. To utilize their outstanding properties in applications, they need to be dispersed. But they are insoluble in many liquids, making their even dispersion difficult.
Scientists at Japan's Kyushu University developed a technique that "exfoliates" aggregated clumps of CNTs and disperses them in solvents. It involves wrapping the tubes in a polymer using a bond that does not involve the sharing of electrons. The technique is called non-covalent polymer wrapping. Whereas sharing electrons through covalent polymer wrapping leads to a more stable bond, it also changes the intrinsic desirable properties of the carbon nanotubes. Non-covalent wrapping is thus considered superior in most cases because it causes minimum damage to the tubes.
The scientists, Dr. Tsuyohiko Fujigaya and Dr. Naotoshi Nakashima, conducted a research review to analyze the various approaches of polymer wrapping and to summarize the applications in which polymer-wrapped carbon nanotubes can be used. Their review has been published in STAM 16-2 p24802, 2015.
They found that a wide variety of polymers can be used for the non-covalent wrapping of carbon nanotubes. Recently, many polymer dispersants have indeed been developed that not only disperse the CNTs but also add new functions to them. These polymer dispersants are now widely recognized and utilized in many fields, including biotechnology and energy applications.
CNTs that are stably wrapped with biocompatible materials are very attractive in biomedicine, for example, due to their incredible ability to pass biological barriers without generating an immune response. There is thus high potential for polymer-wrapped CNTs in the area of drug delivery.
Also, wrapping carbon nanotubes in polymers improves their photovoltaic functions in solar cells, for example, when the polymers function like a light-receiving pigment.
Because the designs of polymers can be readily tailored, it is expected that the functionality of polymer-wrapped CNTs will be further expanded and that novel applications using them will be developed.
####
About Science and Technology of Advanced Materials
Science and Technology of Advanced Materials (STAM) is the leading open access, international journal for outstanding research articles across all aspects of materials science. Our audience is the international materials community across the disciplines of materials science, physics, chemistry, biology as well as engineering.
The journal covers a broad spectrum of materials science research including functional materials, synthesis and processing, theoretical analyses, characterization and properties of materials. Emphasis is placed on the interdisciplinary nature of materials science and issues at the forefront of the field, such as energy and environmental issues, as well as medical and bioengineering applications.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Tsuyohiko Fujigaya
The World Premier International Research Center Initiative
International Institute for Carbon-Neutral Energy Research (WPI-I2CNER)
Kyushu University
Mikiko Tanifuji
Publishing Director
Science and Technology of Advanced Materials
Copyright © ACN Newswire
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() More information about the research paper:
More information about the research paper:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanotubes/Buckyballs/Fullerenes/Nanorods/Nanostrings/Nanosheets
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
![]() Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








